Fig. 1. Schematic of the proposed brain-controlled assistive hearing device.
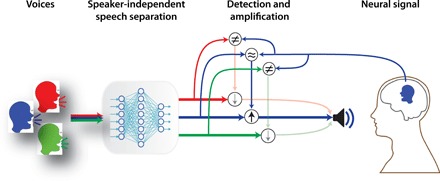
A brain-controlled assistive hearing device can automatically amplify one speaker among many. A deep neural network automatically separates each of the speakers from the mixture and compares each speaker with the neural data from the user’s brain to accomplish this goal. Then, the speaker that best matches the neural data is amplified to assist the user.
