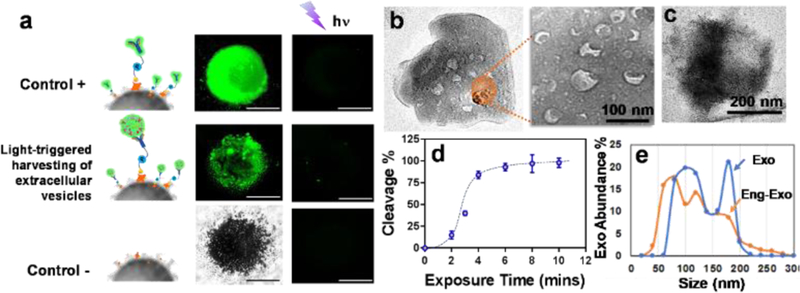
Fig. 4.
a) Characterization of the performance of on-demand photo-release of captured exosomes from immunomagnetic beads. The positive control is a fluorescence-labeled antibody captured by photo-release immunomagnetic beads. The negative control is the immunomagnetic beads without a photo-cleavable linker. b) The SEM image of the surface of photo-release immunomagnetic beads captured with exosomes. Exosome particles were seen as the cup shape due to the vacuum sample preparation. c) The SEM image of the surface of photo-release immunomagnetic beads after photocleavage. d) Characterization of UV exposure time influence on photo-cleavage efficiency. The error bar shows the three repeats with average measurement (RSD < ~5%). e) Nanoparticle tracking analysis of exosome size distribution between photo-released, surface engineered exosomes and native exosomes.