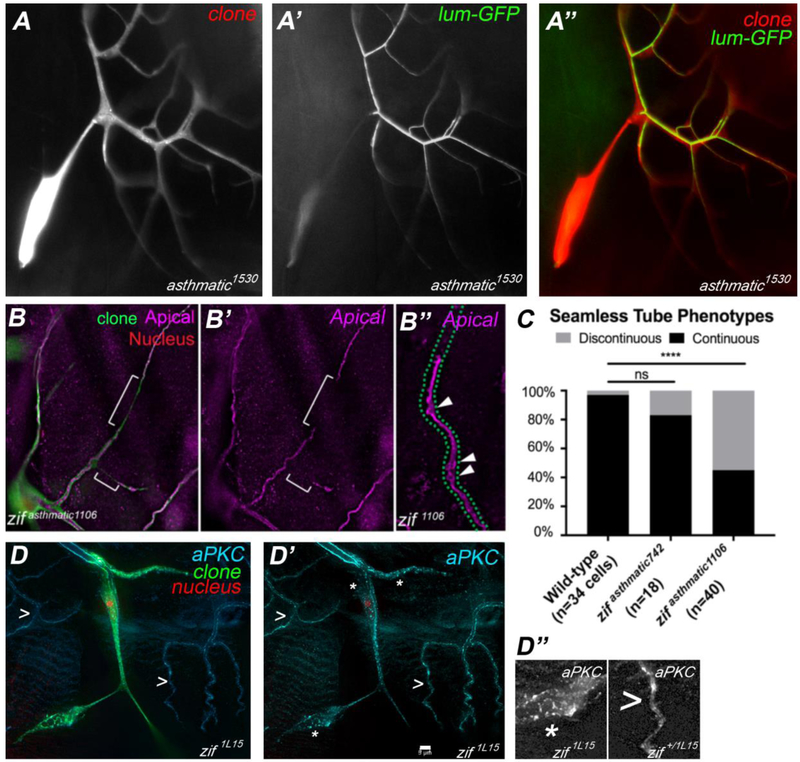
Figure 7: Mutations in zif disrupt maintenance of apical polarity in seamless tubes.
Terminal cells mutant for asthmatic (A, red in A”) lack gas-filled tubes; however, they do make tubes that lack gas-filling, as revealed by the localization of a secreted GFP – lum-GFP – in the lumenal space (A’, green in A”). Mapping studies revealed that asthmatic1530 (shown in A-A”) is not part of the same complementation group as asthmatic742 and 1106, which we now identify as new alleles of zif. We will henceforth refer to only 1530 as asthmatic and rename the 742 and 1106 as alleles of zif. Staining of apical membranes in zif1106 terminal cells (B-B”), reveals the presence of tube shape irregularities (arrowheads in B”) and discontinuities (indicated by [ in B and B’). Discontinuity defects were quantified in (C). To determine the null phenotype, we examined zif1L15 mutant terminal cells (green, D). We found that seamless tubes were largely absent or were severely truncated and that apical membrane antigens such as aPKC (cyan) and Wkdpep (not shown) were no longer enriched on the lumenal membrane, but were dispersed throughout the cell (D and D’). The location of the terminal cell nucleus is revealed by expression of DsRED2nls (red, D). Note that apical membrane localization of aPKC in neighboring heterozygous terminal cells is intact (> in D, D’). In D” adjacent sections of the panel in D’ are shown enlarged (*, portion of zif clone, > portion of zif+/− control cell). Scale Bar (D’) = 5 microns, applies to A-D’.