Figure 1.
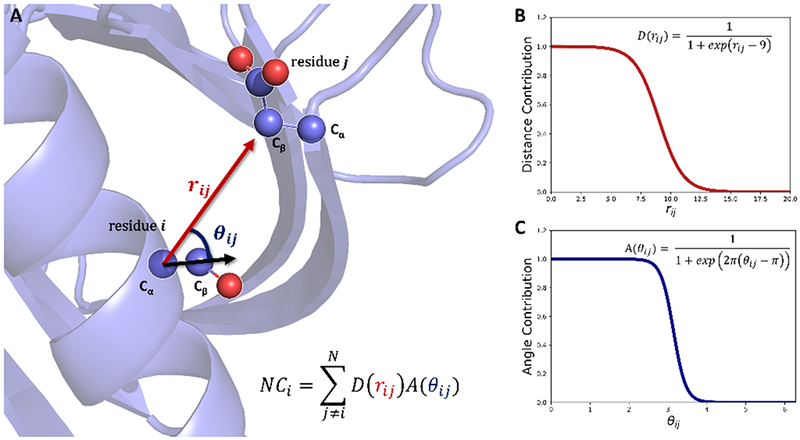
(A) Diagram of the “cone” neighbor count method using the full-atom definition. The neighbor count of residue i is defined as the product of the distance contribution (D(rij)) and the angle contribution (A(θij)) summed over all residues j ≠ i. The distance rij is defined as the length of the vector between the Cα of residue j and the Cβ of residue j and the angle θij is defined as the angle between the vector between the Cα of residue i and the Cβ of residue j and the vector between the Cα and Cβ of residue i. (B) Functional form of the distance contribution, D(rij). (C) Functional form of the angle contribution, A(θij).
