Figure 4. Diagramatic providing a summary of how STRA6 acts to mediated RBP4-induced metabolic disease.
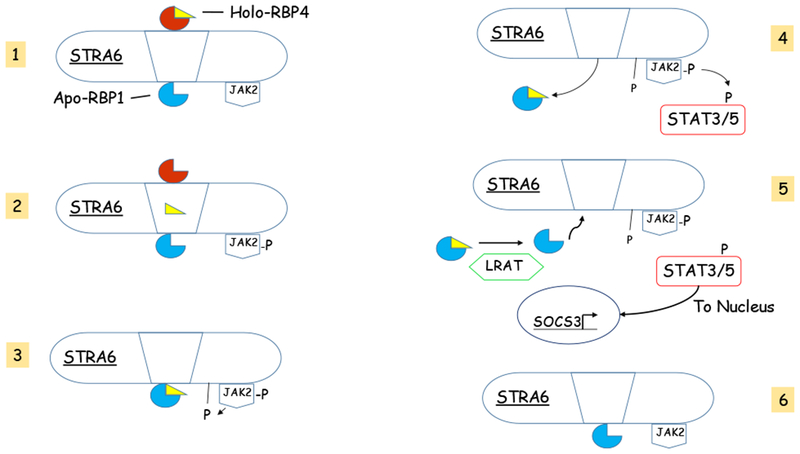
The process is depicted as involving six steps. The mechanism links vitamin A uptake by STRA6-expressing cells with a signaling cascade that regulates expression of multiple STAT target genes. Step 1 commences with the binding of holo-RBP4 to its binding site on the extracellular surface of STRA6. STRA6 is primed with apo-RBP1 bound to its intracellular side. In Step 2 retinol is released by RBP4 and traverses through a pore in STRA6. The movement of retinol is proposed to trigger the phosphorylation of JAK2. Phospho-JAK2 initiates Step 3 which results in the phosphorylation of STRA6 and the frees RBP1 to be released from STRA6. This is followed by Step 4 where holo-RBP1 is released from STRA6 and STAT3 or STAT5 are recruited and undergo activation through phosphorylation by phospho-JAK2. In Step 5, holo-RBP1 delivers retinol to LRAT which converts the retinol to retinyl ester releasing apo-RBP1. This occurs concurrently with the movement of activated phospho-STAT3/5 to the nucleus where it induces expression of STAT target genes including suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3). This results in an inhibition of insulin signaling and PPARg activation. Step 6 involves the binding of apo-RBP1 to STRA6 and the dephosphorylation of JAK2 and STRA6, priming STRA6 for another round of binding with holo-RBP4. Figure 4 was adapted from [(Noy 2016b)].
