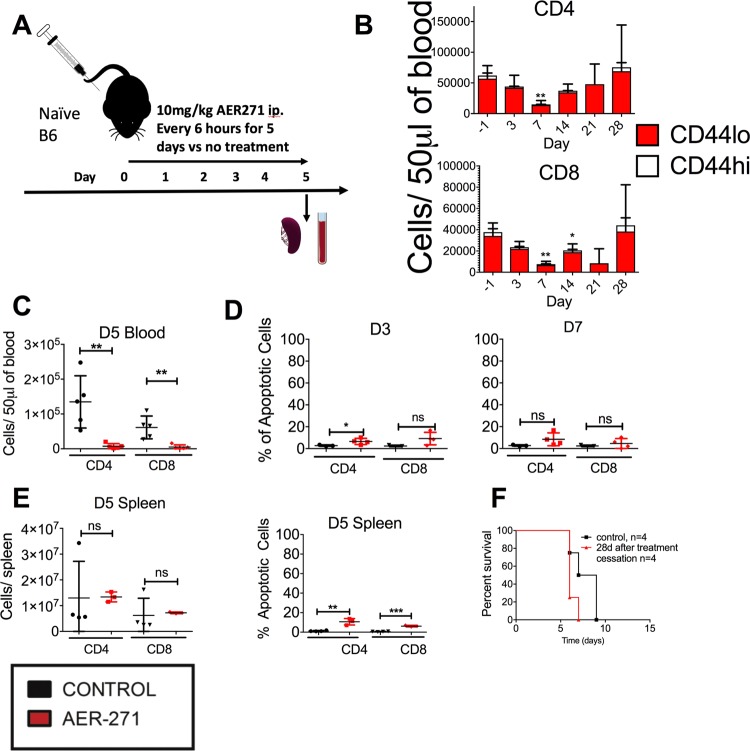
Figure 2.
AER-271 treatment reduces numbers of circulating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (A) Naïve B6 mice were injected with 10 mg/kg AER-271 or PBS i.p. every 6 hours for 5 days (A). The numbers of CD4+ (red) and CD8+ (blue) T cells in peripheral blood were quantified in PBS treated controls (black) and AER-271 treated (red) (B,C) (N = 4–6 animals/group. The experiment was performed 4 times with similar results). (D) Apoptosis rates of peripheral blood CD4 and CD8 T cells determined by caspase-3 activity staining (N = 3–4 animals/group). (E) The numbers and rates of apoptosis of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the spleen (N = 3–4 animals/group). (F) B6 mice were treated with AER-271 for 5 days as outlined in (A). 28 days after treatment initiation, peripheral blood T cells returned to pretreatment levels, control mice were treated with PBS in line with the AQP4 inhibition protocol and then allowed to rest to the same time point. At that time point, the animals were transplanted with fully MHC-mismatched heterotopic heart allografts from BALB/c donors (n = 4 animals/group). (Heart allograft survival was compared between recipient groups by using Kaplan-Meier analysis. All other results were analyzed by using a one-tailed Student t-test where, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, no notation indicates no significant change).