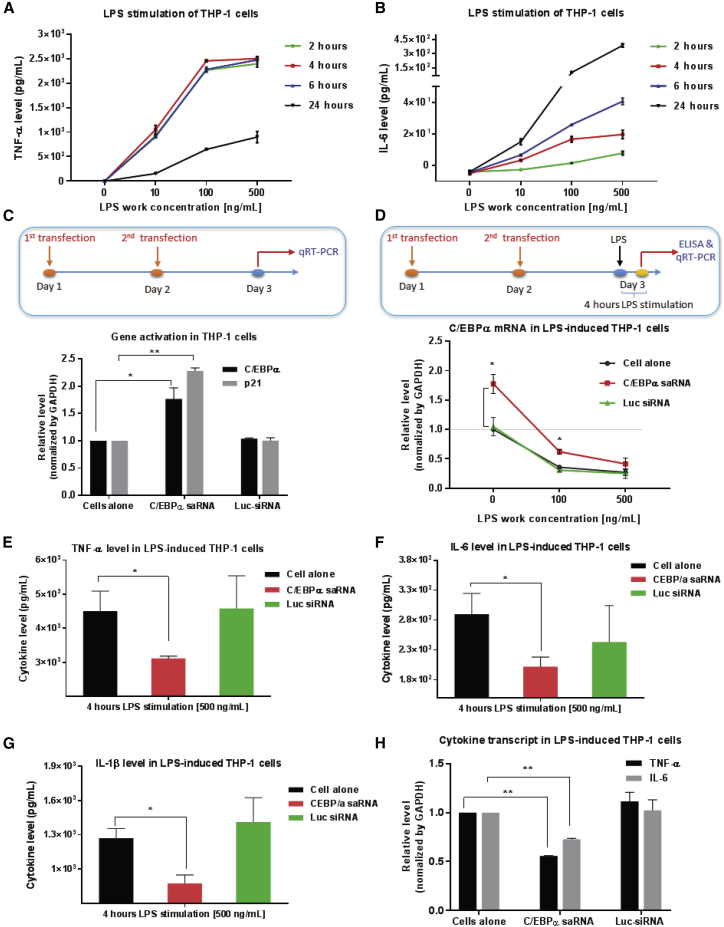
Figure 1.
CEBPA-51 Induces Specific Gene Activation and Suppresses Pro-inflammatory Cytokine Production in LPS-Stimulated THP-1 Monocytes
(A and B) LPS-mediated cytokines production was time and LPS dose dependent. THP-1 cells were treated with different concentrations of LPS. Cell-free supernatant was collected at various time points for quantitative analysis of the pro-inflammatory cytokines (A) TNF-α and (B) IL-6 by ELISA. (C) CEBPA-51 mediated specific gene activity in THP-1 cells. THP-1 cells were transfected with 10 nM CEBPA-51 or control Luc-siRNA twice with Lipofectamine 3000. At 24 h after the last transfection, total RNA was collected for quantitative analysis of target gene C/EBPα and its downstream gene p21 by qRT-PCR assay. (D) CEBPA-51 attenuated LPS-induced downregulation of C/EBPα. The THP-1 cells transfected with 10 nM of experimental RNAs twice were stimulated with different concentrations of LPS for 4 h. Total RNA was collected for qRT-PCR and cell-free supernatant was collected for ELISA. (E–G) CEBPA-51 inhibited the secretion of the soluble pro-inflammatory cytokines (E) TNF-α, (F) IL-6, and (G) IL-1β. (H) CEBPA-51 repressed the transcript RNA expression of cytokines TNF-α and IL-6. Each in vitro experiment was performed at least in triplicate. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns, no significant difference. Analysis with two-tailed Student’s t test.