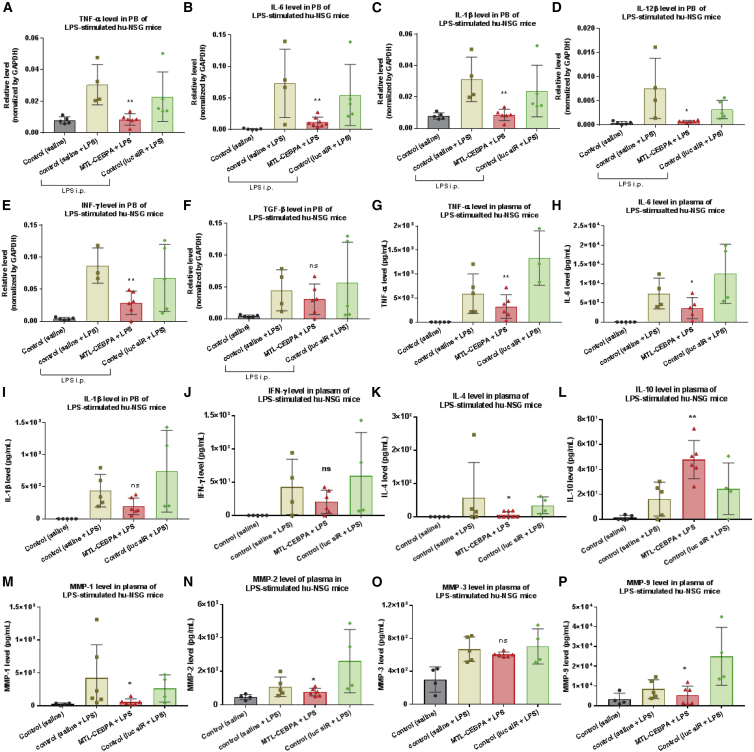
Figure 7.
MTL-CEBPA Inhibits Pro-inflammatory Cytokine Production in an LPS-Stimulated Humanized NSG Model
As described in Figure 6A, at the end of LPS stimulation, animals were sacrificed, whole-blood samples were collected, and cellular and plasma fractions were separated for cytokine profiling analysis by qRT-PCR and Luminex assay, respectively. (A–F) MTL-CEBPA treatment downregulated mRNA expression of the cellular pro-inflammatory cytokines (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-1β, (D) IL-12β, and (E) IFN-γ, but did not significantly change (F) TGF-β. (G–P) The effect of MTL-CEBPA treatment on secretion of soluble inflammatory mediators in mouse plasma was measured by Luminex assay. MTL-CEBPA treatment resulted in a decline of the pro-inflammatory cytokines (G) TNF-α, (H) IL-6, and (K) IL-4 and the MMPs (M) MMP1, (N) MMP2, and (P) MMP9. There was no significant change in the production of (I) IL-1β, (J) IFN-γ, and (O) MMP3. (L) MTL-CEBPA promoted the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine. Each determination analysis was performed in duplicate. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns, no significant difference. Analysis by two-tailed Student’s t test.