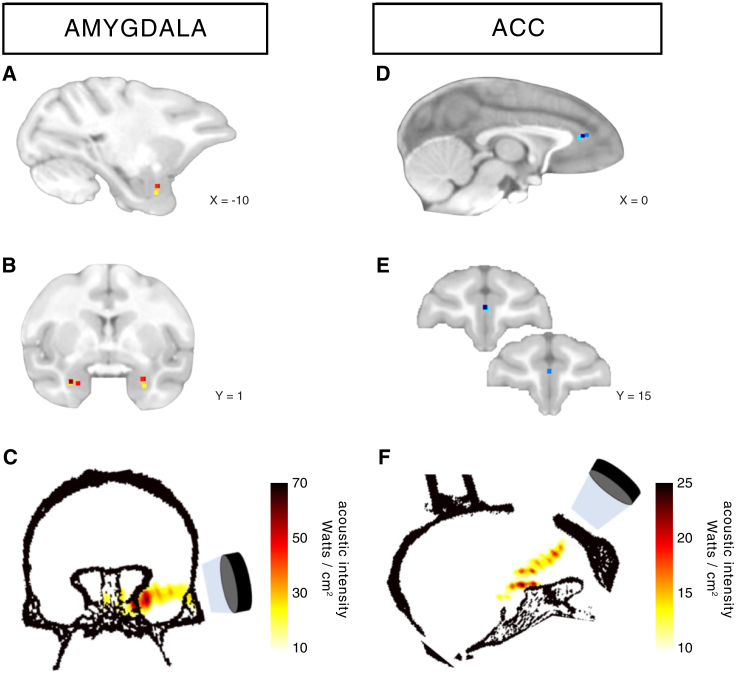
Figure 1.
Stimulation Targets
(A–F) Stimulation target position is shown for each individual animal (colored dots) on sagittal and coronal views for TUS targeted at amygdala (A and B) and ACC (D and E). Acoustic intensity field (W/cm2) generated by the ultrasound beam in the brain is shown for one example animal per TUS target, amygdala (C) and ACC (F). The target position can be delineated with accuracy in all animals in (A), (B), (D), and (E) by using each individual’s own MRI scan. As a result, the activity and functional connectivity of the target areas can be examined accurately in each animal. However, some slight imprecision in the estimation in the acoustic intensity maps in (C) and (F) may occur; this is because group average targets are used in conjunction with the computed tomography X-ray scan of a single individual during the modeling.