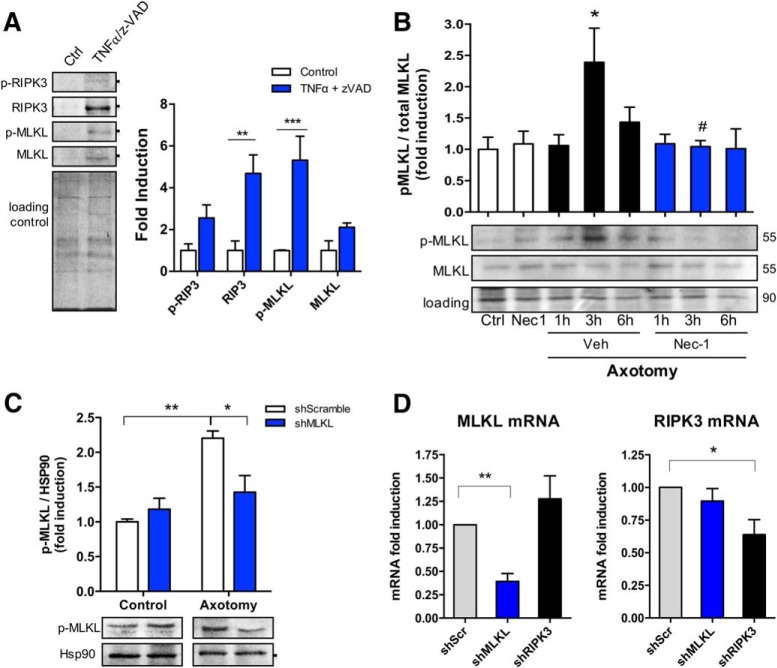
Figure 6.
Necroptosis is activated after axonal injury. Necroptotic pathway activation was evaluated after TNFα/z-VAD treatment through the detection of RIPK3, MLKL, and their phosphorylated forms by Western blot. A, Total protein (Coomassie staining) was used as a loading control to normalize the expression of the different proteins, which were expressed as fold induction compared with control (n = 3). Downstream activation of the pathway was determined in mechanically injured axons in a time course (≤6 h) through the detection of MLKL and p-MLKL. Results are represented as pMLKL/MLKL ratio from n = 5 independent experiments. Total protein was used as a loading control. Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey, * indicates statistically significant compared with Ctrl; # indicates statistically significant compared with 3 h+Veh. B, C, Specificity of p-MLKL antibody was tested in injured axons devoid of MLKL by using DRGs transduced with lentiviral vectors containing MLKL shRNA (B) and compared with a control nontargeting shRNA (scramble; n = 3; C). D, The magnitude of MLKL or RIPK3 knock-down was evaluated by real-time qPCR in dissociated DRGs transduced with lentivirus containing shMLKL or shRIPK3, respectively (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey, * indicates significant compared with Scramble shRNA.