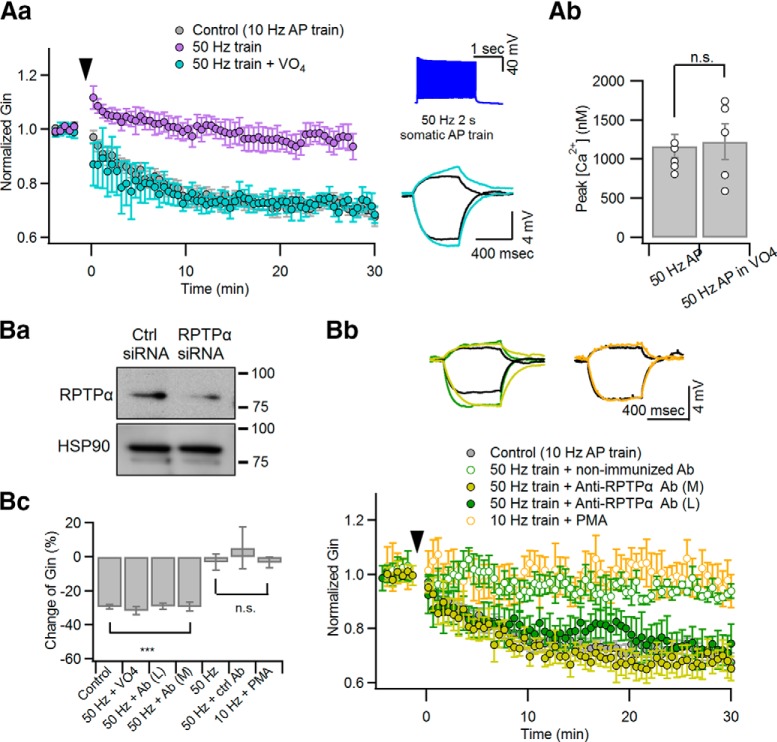
Figure 3.
Inhibition of PTP enables inadequate stimulation to induce LTP-IE. Somatic current pulse injection for 2 s, which elicits a 50 Hz AP train, was used as an inadequate conditioning stimulation. For inhibition of PTP, 100 μm Na3VO4 or anti-RPTPα antibody (1 μg/ml) was added to the whole-cell patch pipette. Aa, Relative changes of Gin caused by a 50 Hz AP train was delivered at 0 s with (cyan) or without (purple) Na3VO4 in the patch pipette. The LTP-IE caused by the 50 Hz AP train in the presence of intracellular Na3VO4 was similar to the somatic conditioning (10 Hz for 2 s, gray), which was reproduced from Figure 1A for comparison. Insets, AP responses to 50 Hz 2 s somatic AP train (top) and subthreshold voltage responses for measuring Gin with the same color code as the main panel (bottom; black, control). Ab, The peak values for distal dendritic [Ca2+]i evoked by a 50 Hz AP train are compared between conditions with or without intracellular Na3VO4. Ba, Test for specificity of the anti-RPTPα antibody. Ctrl siRNA, Nontargeting siRNA; RPTPα siRNA, RPTPα-targeting siRNA. Bb, Relative changes of Gin caused by a 50 Hz AP train with intracellular application of anti-RPTPα antibody (green filled symbols) or isotype antibody (green open symbols). In addition, the effects of PMA on Gin changes after a 10 Hz AP train are superimposed (orange). For comparison, somatic conditioning-induced ΔGin (gray) was reproduced from Figure 1A. Insets, Subthreshold voltage responses for measuring Gin with the same color codes as the main panel. Bc, Summary for ΔGin measured at 30 min after different conditionings: 10 Hz AP train (control), 50 Hz AP train (50 Hz), 50 Hz AP train with intracellular Na3VO4 (50 Hz + VO4), anti-RPTPα AbL (50 Hz + AbL), anti-RPTPα AbM (50 Hz + AbM), non-immunized Ab (50 Hz + ctrl Ab) and 10 Hz AP in the presence of PMA (10 Hz + PMA). n.s., No statistical significance. ***p < 0.005.