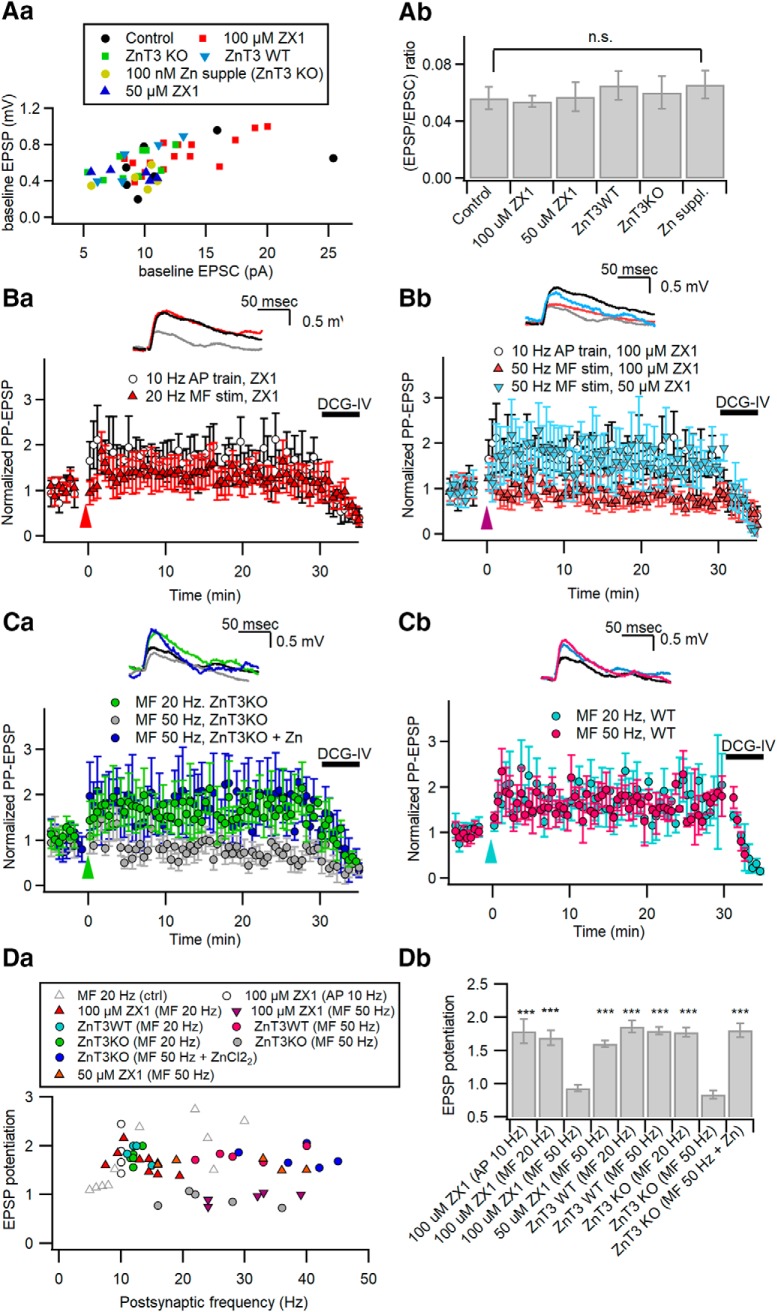
Figure 8.
Zn2+ facilitates MF-induced heterosynaptic potentiation of PP synaptic inputs. Aa, Ab, The relationship between PP-EPSP and PP-EPSC amplitudes measured at the same CA3-PCs (Aa), and the mean values for the EPSP/EPSC ratio (Ab) at PP-CA3 synapses under the conditions tested in Ba to Cb (control, control conditions in CA3-PCs of Sprague Dawley rats; ZX1, in the presence of 100 or 50 μm ZX1 in Sprague Dawley rats; ZnT3KO and ZnT3WT, ZnT3 KO mice and their littermates; Zn suppl., ZnT3 KO with supplement of Zn2+). Ba, Bb, Relative amplitudes of PP-EPSPs before and after MF stimulation at 20 Hz (Ba) or at 50 Hz (Bb) in the presence of 100 or 50 μm ZX1. Data for PP-CA3 EPSPs after somatic conditioning (10 Hz AP train for 2 s) are repeated in Ba and Bb as a control (open circles). Amplitudes are normalized to their mean baseline values. Conditioning MF stimuli were delivered at t = 0 (arrowhead). Ca, Cb, Relative amplitudes of PP-EPSPs before and after MF stimulation at 20 or 50 Hz in CA3-PCs from ZnT3-KO mice (Ca) or their WT littermates (Cb). MF stimulation at 20 Hz (green), but not at 50 Hz (gray), induced LTP of PP-EPSPs in KO CA3-PCs (Ca). Supplement of ZnCl2 rescued the incompetence of 50 Hz MF stimulation in KO (blue). In contrast, MF stimulation induced LTP of PP-EPSPs both at 20 and 50 Hz in WT CA3-PCs (Cb). Ba–Cb, Insets, PP-EPSP traces before (gray) and 25 min after a conditioning (same color codes as in main panels). Da, Plot of PP-EPSP potentiation as a function of the number of postsynaptic APs elicited by conditioning stimuli, as indicated in the boxed graph legend. MF-induced potentiation of PP-EPSPs under control conditions (gray triangles) are reproduced from Hyun et al. (2015) for comparison. Db, Summary for potentiation of PP-EPSPs induced by different conditionings. n.s., No statistical significance. ***p < 0.005.