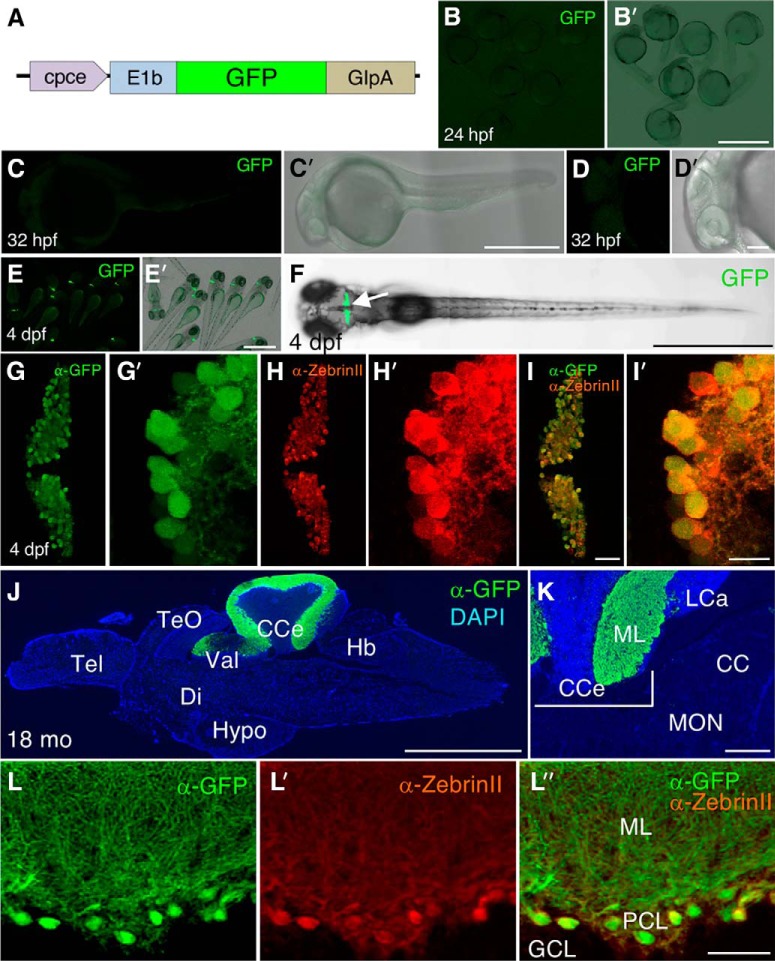
Figure 5.
Characterization of GFP expression pattern of Tg(cpce-E1b:GFP)bz13. A, Schematic drawing of construct carrying the cpce-E1b promoter and driving GFP expression used to establish the Tg(cpce-E1b:GFP)bz13 transgenic strain. GFP reporter expression is not detectable in embryos at 24 (B, B′) and 32 hpf (C, C′, D, D′). In contrast to Tg(-7.5ca8:GFP)bz12 larvae that show ectopic expression (Fig. 3), GFP expression is restricted to the cerebellum (F, arrow) in 4 dpf larval Tg(cpce-E1b:GFP)bz13 zebrafish (E, E′, F). Co-immunostaining with anti-GFP (G, G′, green) and anti-ZebrinII (H, H′, red) antibodies reveals PC-specific expression of GFP in PCs at 4 dpf in merged images (I, I′). J, Sagittal section of an adult 18-month-old brain from Tg(cpce-E1b:GFP)bz13 fish showing immunostaining of GFP (green) in the cerebellum and DAPI counterstaining (blue). K, Higher-magnification of the MON reveals lack of GFP expression in this cerebellar-like structure compared with the PCL in the adjacent CCe. L, L′, L″, GFP-positive (green) cells are detected as ZebrinII-positive PCs (red). Scale bars: B′, E′, F, J, 1 mm; C′, 500 μm; K, 200 μm; D′, 100 μm; I, L″, 50 μm; I′, 10 μm. CC, Crista cerebellaris; CCe, corpus cerebelli; Di, diencephalon; GCL, granule cell layer; Hb, hindbrain; Hypo, hypothalamus; LCa, lobus caudalis cerebelli; ML, molecular layer; PCL, PC layer; Tel, telencephalon; TeO, optic tectum; Val, lateral division of the valvula cerebelli.