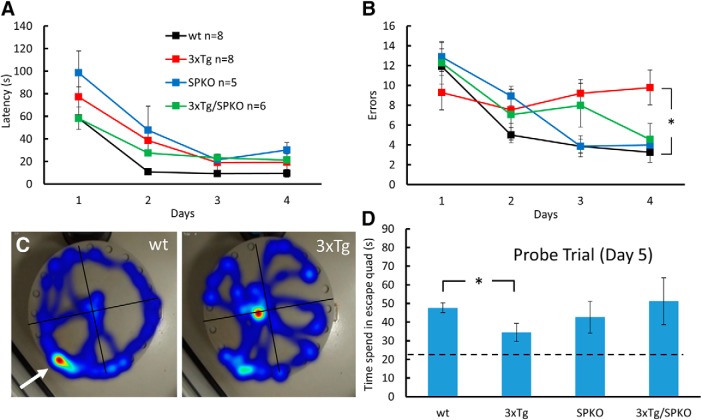
Figure 7.
SP deficiency restores spatial navigation in the 3xTg mice: 7-month-old male mice were trained in the Barnes circular maze for 4 d. A probe trial, in which the escape hole was blocked (C, white arrow), was conducted 24 h after the last training session. A, B, During acquisition phase, latency (A) and errors (B) were recorded. During the probe trial, time in the escape quadrant was recorded. All groups learned this task. C, However, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA revealed a significant effect for groups on errors (F(8.36,66.86) = 2.928, p = 0.038), and a Tukey HSD post hoc test indicated a significant difference between 3xTg and wt groups (p = 0.023). D, In the probe trial, all groups displayed a search bias for the target quadrant (dashed line indicates chance level); however, a one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc test indicated a significant difference between the groups (wt, 47.68 ± 2.653 s; 3xTg, 34.4 ± 4.92 s; F15 = 4.159, p = 0.032). *p < 0.05.