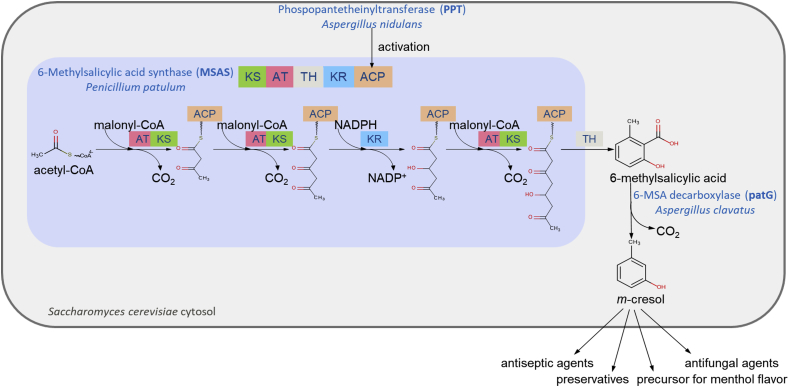
Fig. 1.
Metabolic pathway for m-cresol production in S. cerevisiae via 6-methylsalicylic acid (6-MSA) synthesis. The 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase (MSAS) consists of multiple domains: the ketoacylsynthase (KS), acyltransferase (AT), thioester hydrolase (TH), ketoreductase (KR), and acyl carrier protein (ACP). MSAS must be activated by phosphopantetheinylation, and catalyzes the synthesis of 6-MSA from one acetyl-CoA and three malonyl-CoA under consumption of one NADPH. 6-MSA decarboxylase can further convert 6-MSA to m-cresol, valuable for the flavor and pharmaceutical industry. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)