Fig. 8.
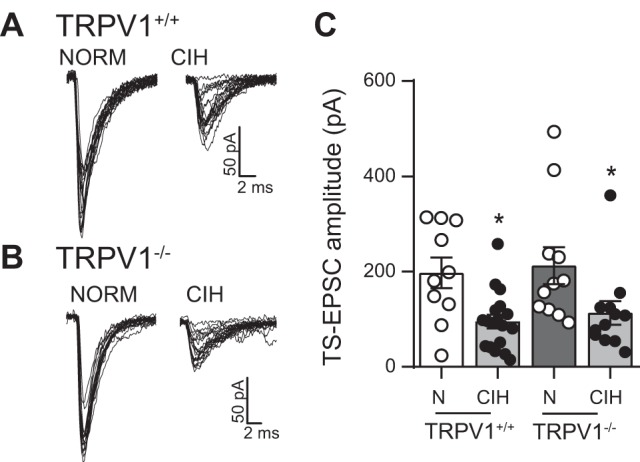
Tractus solitarii-evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents (TS-EPSCs) of TRPV1+/+ and TRPV1−/− neurons of nucleus tractus solitarii (nTS) are similar under normoxia (NORM) and both decrease following chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH). A and B: TS-EPSCs in NORM were similar in TRPV1+/+ and TRPV1−/− mice. However, in both mice, the amplitude of the evoked response is reduced by CIH exposure. Examples are overlays of 20 traces each. C: mean data of TS-EPSCs in TRPV1+/+ and TRPV1−/− mice in NORM (N) and following CIH. As shown in our example, CIH decreased TS-EPSC amplitude to a comparable amplitude (2-way ANOVA: hypoxia, P = 0.004; mouse, P = 0.53; hypoxia × mouse, P = 0.96). *P < 0.05, CIH vs. NORM with Bonferroni post hoc (TRPV1+/+: NORM, n = 10; CIH, n = 18; TRPV1−/−: NORM, n = 11; CIH, n = 12).
