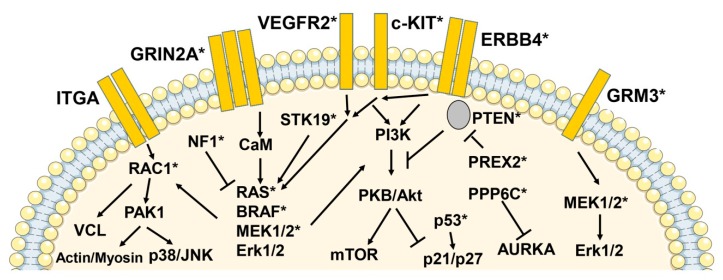
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of signaling pathways with activating and inactivating mutations or gene amplifications in melanoma. In large-scale sequencing studies using next-generation sequencing a number of activating and inactivating mutations and gene amplifications of genes encoding for intracellular signaling molecules could be identified, apart from BRAF and NRAS. A schematic representation of these molecules and pathways is shown. Protein products of mutated or amplified genes are indicated by asterisks. Abbreviations: ITGA, integrin alpha; GRIN2A, glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-1; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; KIT, v-Kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; ERBB4, Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4; GRM3, glutamate receptor, metabotropic 3; RAC1, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; NF1, neurofibromin 1; STK19, serine/threonine-protein kinase 19; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; PKB, protein kinase B; PREX2, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 2; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; PAK, p21-activated kinase 1; CaM, calmodulin; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; MAP2K1/2 (MEK1/2), mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2; Erk1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, VCL, vinculin; PPP6C, protein phosphatase 6 catalytic subunit; AURKA, aurora kinase A.