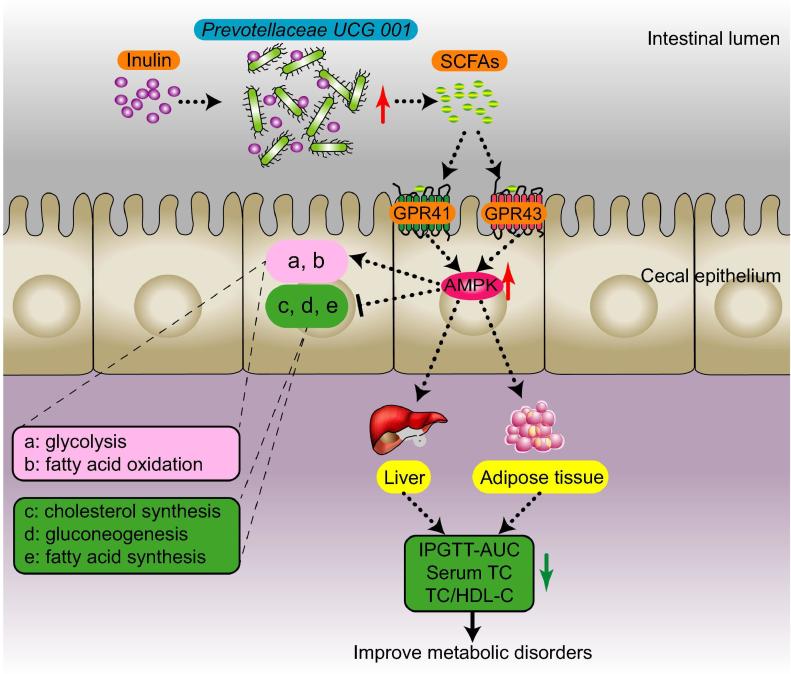
Figure 5.
Presumed mechanism by which inulin alleviated glucose and lipid metabolism disorders in ob/ob mice
The inulin-supplemented diet promotes the proliferation of Prevotellaceae UCG 001 in the gut of ob/ob mice. This strain degrades inulin to produce SCFAs, which recognized GPR41/43 on the surface of intestinal epithelial cells, and lead to activation of the AMPK signaling pathway. Finally, this signal leads to changes in downstream metabolic functions. SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; GPR41/43, G protein-coupled receptors 41/43; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; AUC, area under the curve; IPGTT, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test.