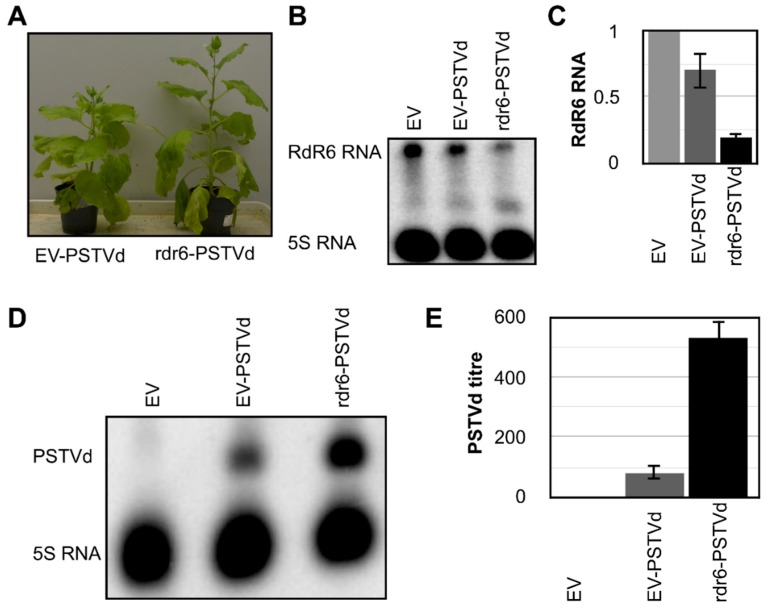
Figure 2.
RdR6 compromised N. benthamiana plants exhibited higher amounts of PSTVd. The RdR6 knocked-down N. benthamiana plants were subjected to a PSTVd-RG1 infection assay in order to verify the role of the RdR6 mRNA in viroid accumulation. (A) At 21 days post-inoculation (dpi), the plants did not exhibit any viroid-associated disease symptoms. Total RNA extracted from N. benthamiana plants at 21 dpi was used to monitor the expression of RdR6 by (B) RNA gel blot and (C) RT-qPCR assay using RdR6 specific radiolabeled probes and primers, respectively. The same RNA sample was also used to evaluate the accumulation of PSTVd RNA by (D) RNA gel blot and (E) RT-qPCR assays using PSTVd specific radiolabeled probes and primers, respectively. In the (E) PSTVd titer represents the quantity of PSTVd RNA obtained by RT-qPCR. The expression change is presented on a log2 scale. The error bars indicate the standard deviation (SD). EV-PSTVd, plants agroinfiltrated with pTRV2-EV vector and infected with PSTVd-RG1; rdr6-PSTVd, plants agroinfiltrated with pTRV2-RdR6 vector and infected with PSTVd-RG1. Each experiment was performed at least three times with true biological replicates.