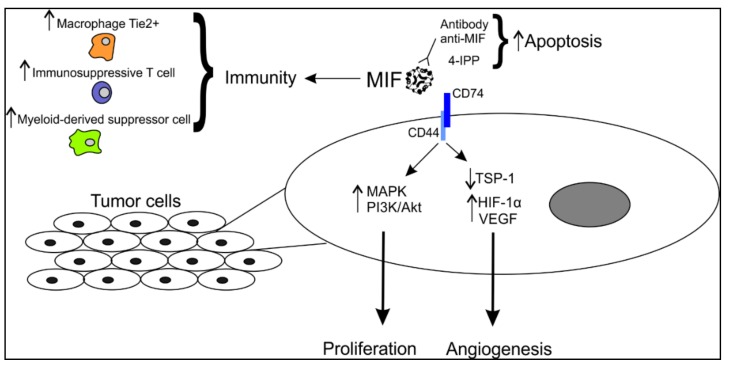
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the involvement of MIF in melanoma cells. MIF is secreted in the microenvironment and can interact with tumor cells via its membrane receptor CD74. In this way, it affects several pathways in proliferation and angiogenesis. MIF can also modulate the anti-tumor immune response by upregulating the expression of specific immune cells playing an immunosuppressive role. MIF, migration inhibitory factor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; TSP-1, thrombospondin 1; HIF-1α, hypoxia-induced factor 1α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.