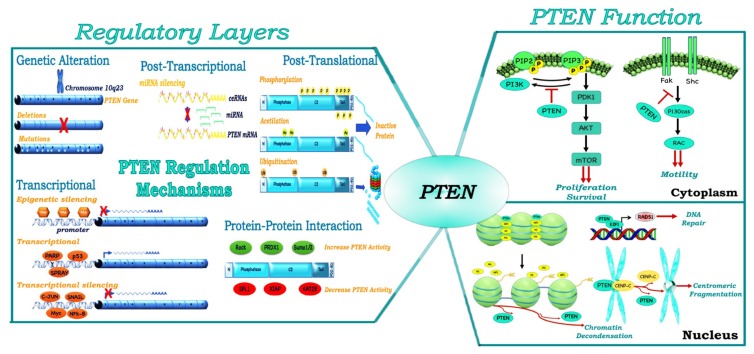
Figure 2.
PTEN protein regulation and function. PTEN protein expression is regulated by genomic (mutation and deletions), transcriptional (epigenetic mechanisms and transcription factors), post-transcriptional (miRNAs, PTEN pseudogene), post-translational mechanisms (phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, etc.) and protein–protein interaction. PTEN performs multiple cellular functions, at least in part determined by its subcellular localization. In the cytoplasm, PTEN dephosphorylates PhosphatidylInositol-3,4,5-trisPhosphate (PIP3), decreasing PI3K activity and several proteins such as focal adhesion kinase (FAK) or Src-Homology/Collagen (SHC), to regulate different signal networks. The nuclear PTEN activities include the regulation of genomic stability, gene expression, DNA repair mechanisms and centromeric stability.