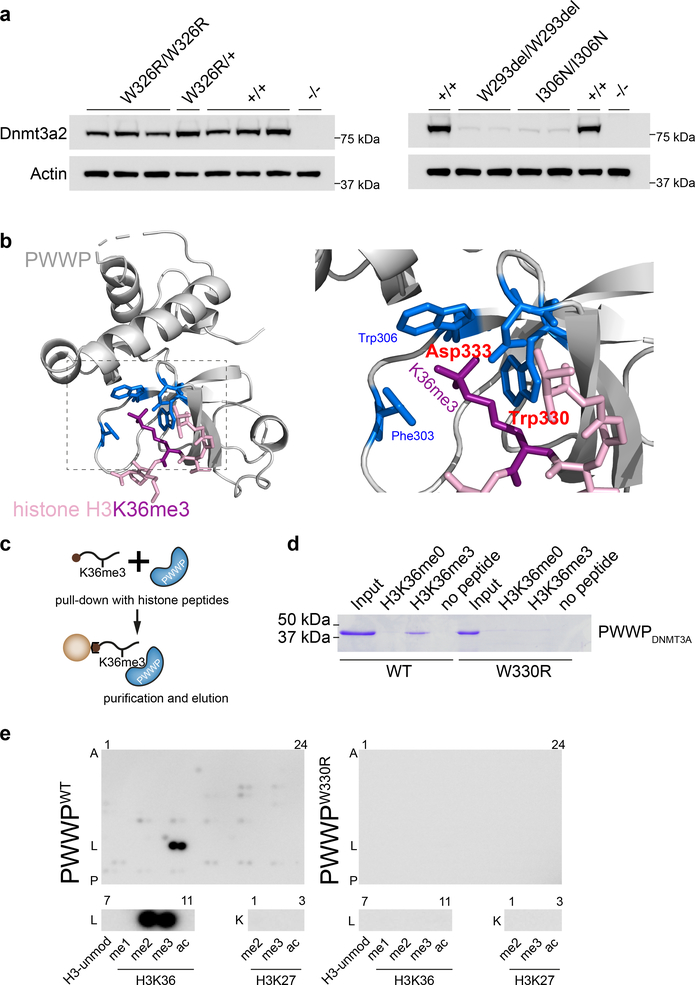
Fig. 2|. The W330R mutation impairs binding of di/tri-methylated H3K36.
a, Murine Dnmt3aW326R protein, containing the orthologous substitution to W330R, is stably expressed, in contrast to corresponding overgrowth PWWP mutations (W293del, I306N). Immunoblotting of cell lysates from CRISPR/Cas9 genome-edited mouse embryonic stem cells (mESC). Multiple independent cell lines, with genotypes as indicated. Representative of n=3 (WT, W326R lines) and n=2 (W293del, I306N) independent experiments. Immunoblots are cropped. b, Structural modelling of the PWWP domain predicts the W330R mutation to disrupt interaction with H3K36me3. The highlighted amino acids (blue) form a cage that binds trimethylated lysine 36 (purple). The amino acids altered in MD patients (tryptophan at codon 330 and aspartate at codon 333) are labelled in red. Backbones of PWWP and histone H3 N-terminal tail depicted in grey and pink respectively. c,d, Recombinant PWWPWT but not PWWPW330R protein binds H3K36me3 peptide. (c) Schematic of streptavidin pull-down of biotinylated histone peptides. (d) Coomassie stained gel of eluted protein from histone peptide pull-downs (cropped). Input, 9% of total protein. Histone peptide H3 (aa 21–44). H3K36me0 corresponding unmodified peptide. Representative of n=3 expts. e, PWWPW330R does not bind H3K36me2, H3K36me3 or other histone-tail modifications. MODified™ Histone Peptide Array representing 384 distinct or combinatorial histone modifications probed with recombinant PWWP proteins as indicated. Below, magnified insets of row L7–11 (histone 3 aa26–45) and K1–3 (histone 3 aa16–35) demonstrates that PWWPWT binds to H3K36me2 (L9) and H3K36me3 (L10), but PWWPW330R does not. Representative of n = 2 independent expts; see also Supplementary Fig. 1b.