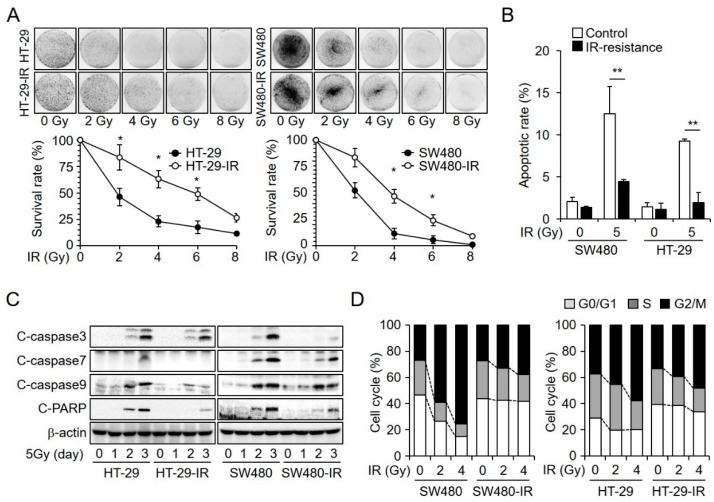
Figure 1.
Establishment and characterization of irradiation-resistant colorectal cancer cell lines. (A) A clonogenic assay revealed that the radiation-resistant cell lines HT-29-IR and SW480-IR showed decreased radiation-induced cell mortality compared to that in the radiosensitive parental cell lines. Both sensitive and resistant cell lines were exposed to 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy gamma-irradiation. (* p < 0.05). (B) Analysis of apoptosis by flow cytometry in radiosensitive and radioresistant cell lines. After exposure to 5 Gy of ionizing radiation for 48 h, comparing it to that in parental cells (** p < 0.05). (C) Western blot analyses were performed to determine the expression levels of cleaved (C) caspase 3, 7, and 9 and cleaved PARP. β-actin was used as an internal control. Parental cells were more sensitive to radiation than the corresponding ionization radiation-resistant cells. (D) Cell cycle distribution of irradiation-exposed cells (SW480, HT-29, SW480-IR, and HT-29-IR cells) for the indicated doses (0, 2, and 4 Gy). Flow cytometry was used to measure cell cycle arrest.