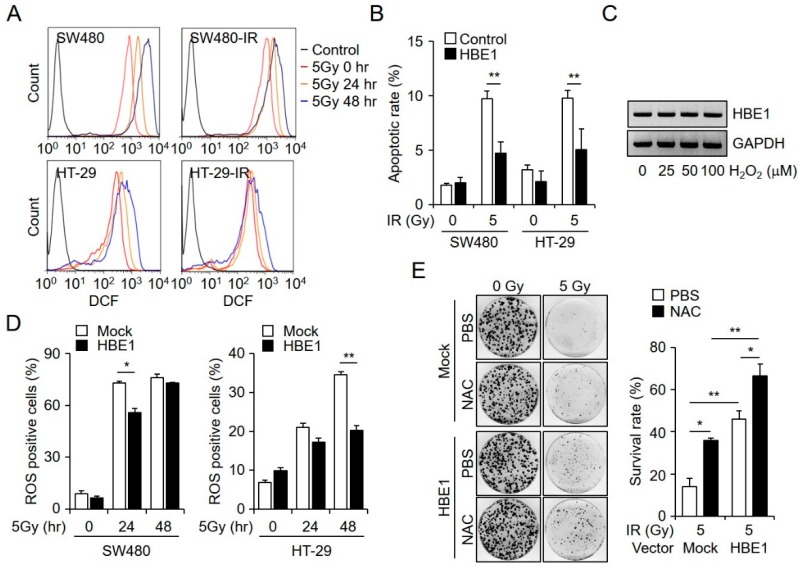
Figure 3.
HBE1 expression inhibits radiation-induced cell death by attenuating reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in colorectal cancer cells. (A) CM-H2DCFDA was used to detect radiation-induced ROS generation by flow cytometry at 24 and 48 h after administering 5 Gy of irradiation. (B) After the stable transfection of SW480 and HT-29 cells with a control or pCMV-HBE1-overexpression vector, radiation-induced cell death was measured by flow cytometry. After 48 h, both cell lines were irradiated with 5 Gy and apoptotic rates were analyzed by annexin V and PI staining. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (C) RT-PCR data showing the dose-dependent induction of HBE1B mRNA levels in H2O2-treated SW480 cells. (D) Intracellular ROS levels in HBE1-overexpressing SW480 and HT-29 based on CM-H2DCFDA and as measured by flow cytometry, at 24 and 48 h after exposure to 5 Gy of irradiation. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (E) Following the transfection of SW480 cells with a mock or HBE1-overexpression vector, a clonogenic assay was performed after treating the cells with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) (10 mM) and exposure to 5 Gy irradiation. The left panel shows a representative clonogenic plate and the right panel depicts the survival rate. All data shown are the means ± SD of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 versus the control.