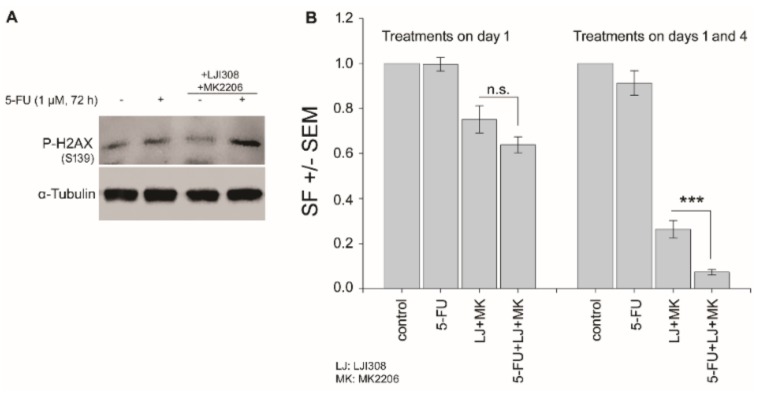
Figure 6.
Dual targeting of the RSK/YB-1 pathway and Akt enhances the clonogenic inactivation by 5-FU in KRAS(G13D)-mutated HCT116 cells. Cells were treated with 5-FU (1 µM), RSK/Akt inhibitors (10 µM of LJI308 and 5 µM of MK2206) or a combination of the inhibitors with 5-FU for 72 h. (A) Level of P-H2AX (S139) was detected by Western blotting. α-Tubulin was detected as loading control. (B) Clonogenic assay was performed as described in the Materials and Methods section. Cells were plated in 6-well plates (250 cells/well) and were treated as indicated either on day 1 (right part of the histogram) or on days 1 and 4 (right part of the histogram). 9 days later, colonies that formed were stained and counted. Survival fractions were calculated as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data represent the mean survival fraction (SF) ± SEM from three biologically independent experiments (18 data) for treatments on day 1 and two biologically independent experiments (12 data) for treatments on days 1 and 4. Asterisks indicated significant inhibition of clonogenic activity by the combination of RSK/Akt inhibitors with 5-FU compared to the effect of RSK/Akt inhibitors alone (*** p ≤ 0.001). n.s.: nonsignificant.