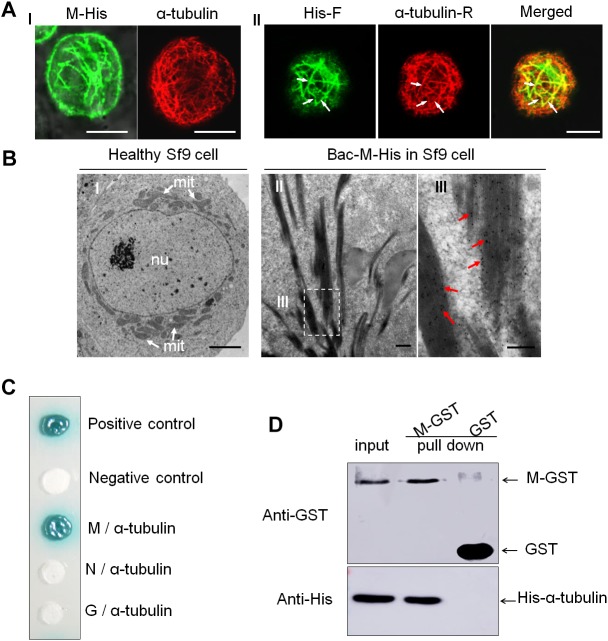
FIGURE 4.
Interaction of RYSV M protein with α-tubulin of N. cincticeps. (A) Expressed RYSV M protein co-localized with α-tubulin in Sf9 cells. (A-I) The RYSV M protein formed tubular structures in Sf9 cells. (left) Samples were immunostained with M-specific antibodies at 30 h post-inoculation (hpi). (right) Healthy, uninfected Sf9 cells treated the same way served as the control, labeled with monoclonal α-tubulin antibodies conjugated with rhodamine (red, α-tubulin-R). (A-II) Samples were immunolabeled with rabbit polyclonal His antibodies conjugated with FITC (green, His-F) and α-tubulin-R. White arrows indicate the co-localization of α-tubulin and RYSV M protein. Scale bars, 15 μm. (B) Electron micrographs showing the subcellular localization of fusion protein M-His at 72 hpi in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells. (B-I) Healthy, uninfected Sf9 cell (control). Scale bar, 2 μm. (B-II) Sf9 cells infected with baculovirus expressing M-His protein and immunolabeled with an M-specific rabbit polyclonal antibody as the primary antibody, then treated with goat-anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with 15 nm diameter gold particles. (B-III) Magnification of the boxed area in (B-II). mit, mitochondria; nu, nucleus. Red arrows, gold particles. Scale bars, 100 nm. (C) Yeast two-hybrid assay analysis of the interaction between the RYSV M protein and N. cincticeps α-tubulin. β-galactosidase activity was detected on a SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade/X-α-gal culture medium. (D) GST pull-down assay to detect the interaction of the RYSV M protein with N. cincticeps α-tubulin.