FIGURE 1.
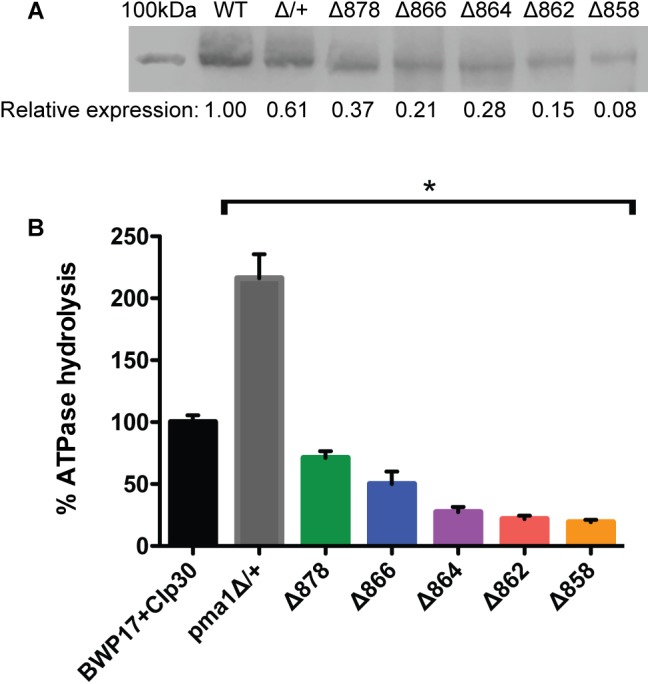
Pma1p truncation mutants have decreased plasma membrane Pma1p levels and decreased plasma membrane ATPase activity. Plasma membranes were isolated from exponentially growing cells via zymolyase- and glass bead-mediated cell wall disruption followed by density-gradient sucrose centrifugation. Plasma membranes were isolated independently in quadruplicate. (A) Western blot using a rabbit primary antibody raised against the N-terminus of S. cerevisiae Pma1p and a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to an IR dye with fluorescence at 800 nm. 100 kDa indicates a 100 kDa marker band (Precision Plus Protein ladder, Bio-Rad) stained with Coomassie blue and captured via measuring fluorescence at 700 nm. The expected size of C. albicans Pma1p is approximately 100 kDa. WT indicates the wild-type control strain, BWP17+CIp30. Western blots were performed independently in triplicate. Relative expression levels were quantified using Licor ImageStudio software and normalized to expression in the wild-type control strain. Pma1p levels decrease with increasing Pma1p truncation in isolated plasma membranes. Pma1p levels are also decreased in a strain heterozygous for PMA1. (B) Percent ATPase-specific activity in isolated plasma membranes as compared to ATPase-specific activity in the BWP17+CIp30 wild-type control. ATPase hydrolysis activity was measured using an enzymatic assay in which the rate of ATP hydrolysis is coupled to the oxidation of NADH, measured as a loss of A340 over time. ATPase assays were performed four times independently, with four technical replicates each time. The average BWP17+CIp30 ATPase-specific activity was 0.30 μmol Pi/min/mg. Increasing C-terminal truncation of Pma1p corresponds to decreased ATPase-specific activity in purified plasma membranes. Deletion of a single allele of PMA1 results in a compensatory increase in ATPase-specific activity. Asterisk (∗) denotes statistical significance (p > 0.01) compared to the BWP17+CIp30 wild-type control in a one-way ANOVA.
