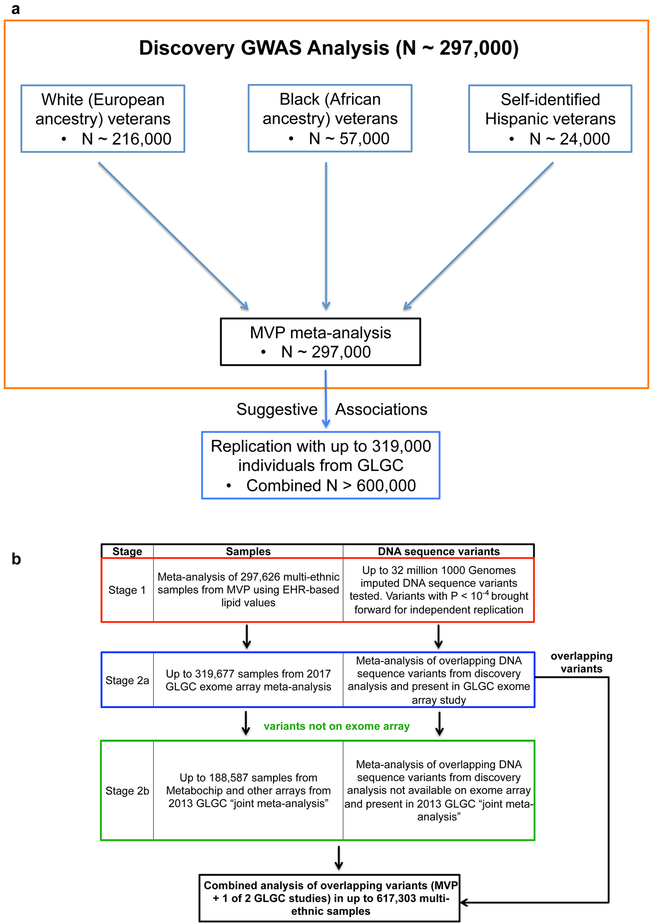
Figure 1. GWAS Study Design.
a) DNA sequence variants across 3 separate ancestry groups in the Million Veteran Program were meta-analyzed using an inverse-variance weighted fixed effects method in the discovery phase (Stage 1). Variants with suggestive association were then brought forward for independent replication.
b) DNA sequence variants with suggestive association (two-sided linear regression P < 10−4) in discovery (Stage 1) were brought forward for independent replication and tested using summary statistics from the 2017 exome-array focused GLGC meta-analysis (Stage 2a). Only variants with suggestive association in Stage 1 that were not present in the GLGC 2017 exome-array study (Stage 2a) were alternatively replicated in the 2013 GLGC “joint meta-analysis” (Stage 2b).
Abbreviations: MVP, Million Veteran Program; GWAS, genome-wide association study; EHR, electronic health record; GLGC, Global Lipids Genetics Consortium