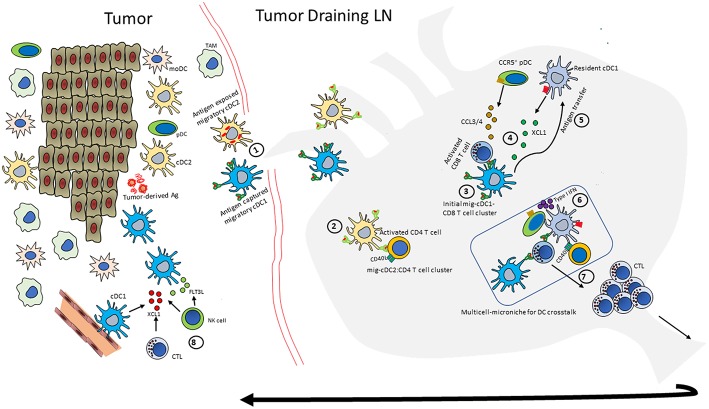
Figure 2.
An integrated model of DC crosstalk for anti-tumor immunity. Outline of the multicellular orchestration of events that can contribute to a robust anti-tumor response. (Note: not all events happen in every context, and the order may also differ). (1) Intratumoral migratory-cDC1 and -cDC2s scavenge tumor-derived antigens and migrate to tumor dLN. (2) migratory-cDC2s (mig-cDC2) present MHC class II-restricted tumor antigen to CD4 T cells and induce expression of molecules such as CD40L (3) Migratory-cDC1s (mig-cDC1) prime and activate naïve CD8 T cells; (4) these activated CD8 T cells produce XCL1 and CCL3/4 to draw in XCR1+LN-resident-cDC1s and CCR5+ pDCs to the site of initial priming. (5) Mig-cDC1s can hand-off antigen to the newly recruited, LN-resident-cDC1. (6) pDCs produce type I IFN to mature cDCs. (7) The licensed CTL with enhanced effector functions undergoes clonal expansion and moves to the tumor to induce tumor cell killing. (8) The activated CD8 T cells and NK cells can mediate further increase in cDC1 numbers by producing XCL1 and FLT3L.