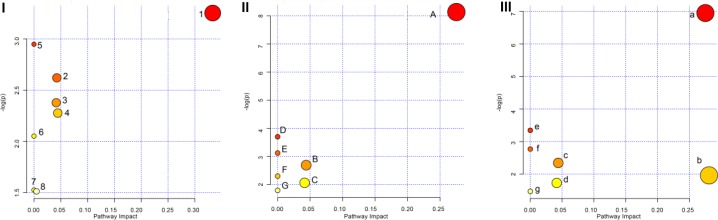
FIGURE 7.
Overview of the pathway analysis for raw and processed GF. Panel (I) shows the pathways of GF, panel (II) shows the pathways of GFP, and panel (III) shows the pathways of GFC. (1) Valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis; (2) Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism; (3) Sphingolipid metabolism; (4) Glycerophospholipid metabolism; (5) Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis; (6) Valine, leucine, and isoleucine degradation; (7) Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis; (8) Purine metabolism. (A) Glycerophospholipid metabolism; (B) GPI-anchor biosynthesis; (C) Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism; (D) Linoleic acid metabolism; (E) alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism; (F) Sphingolipid metabolism; (G) Arachidonic acid metabolism. (a) Glycerophospholipid metabolism; (b) Sphingolipid metabolism; (c) GPI-anchor biosynthesis; (d) Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism; (e) Linoleic acid metabolism; (f) alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism; (g) Arachidonic acid metabolism.