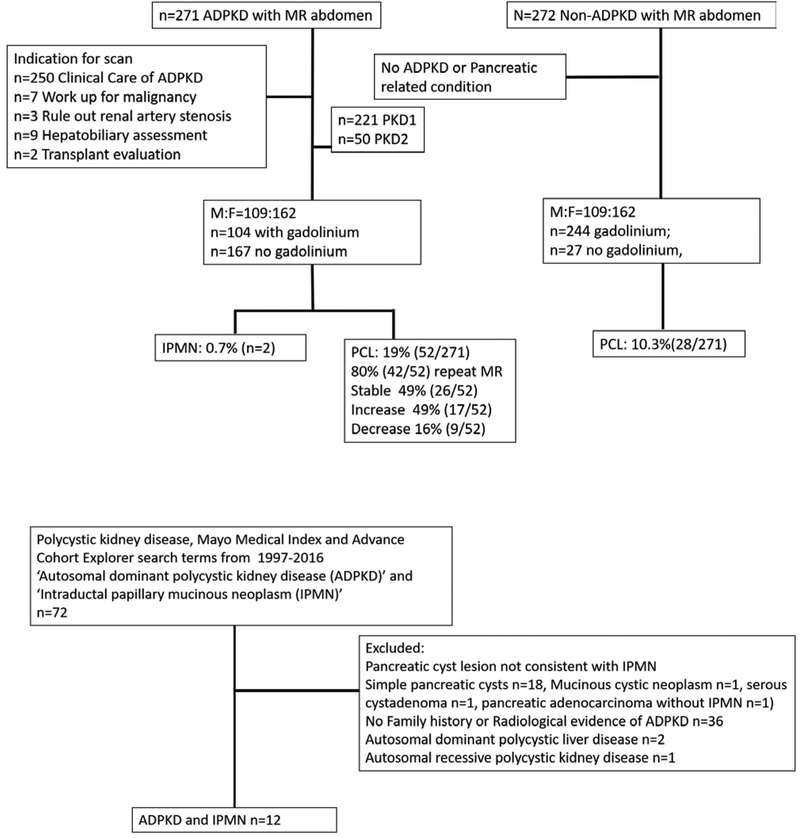
FIGURE 1.
Flowchart of PCLs in the ADPKD Study and the Search Criteria to Identify ADPKD Patients With IPMN. A, The Advanced Cohort Explorer database was used to search for individuals presenting to Mayo Clinic with a diagnosis of PKD and IPMN. Health record review by radiology, gastroenterology, and nephrology services was used to further evaluate and exclude 60 patients as not having PCLs consistent with IPMN or having cystic kidney disease consistent with ADPKD. B, MRI scans of ADPKD patients from Mayo Clinic (n = 271) between February 1998 and October 2013 were compared with age- and sex-matched non-ADPKD individuals (n = 271). ADPKD indicates autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; F, female; IPMN, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; M, male; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PCL, pancreatic cyst lesion; PKD, polycystic kidney disease.