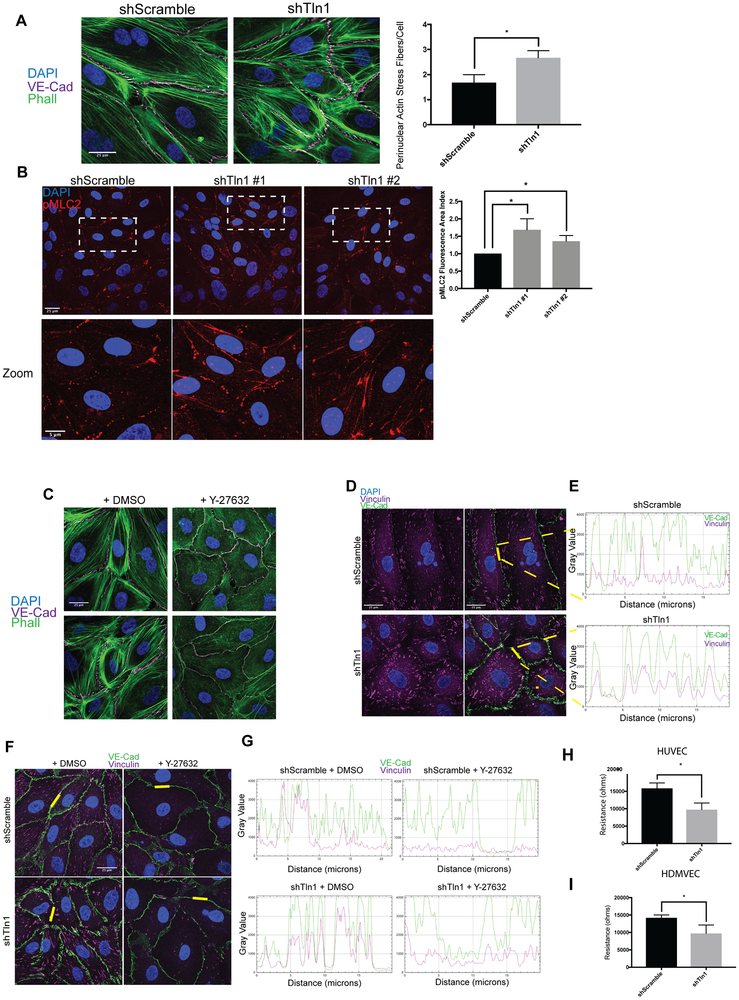
Figure 5: Increased cell contraction and tensile adherens junctions in talin-deficient endothelial cell.
A. Phalloidin and VE-cadherin immunofluorescence on shScramble and shTln1 HUVECs. The number of perinuclear stress fibers per cell were quantified as described in methods. (n=3; scale=25 μm *p=0.016 two-tailed unpaired t-test) B. Max-intensity immunofluorescence projections of HUVECs stained with anti-pMLC2 antibody indicate increased pMLC2+ cell area in shTln1#1 and shTln1#2 cells relative to shScramble (n=2-4; scale=25 μm; *p=0.0105, *p=0.0405 one-way ANOVA with Kruskal Wallis multiple comparisons test) C. Inhibition of cytoskeletal contraction by treating cells with Rho-associated kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (50nM, 12 hours) reduces junctional disorganization and FAJ formation in talin-deficient HUVECs. (n=3; scale=25 μm). D. Co-localization of VE-Cadherin (magenta) and Vinculin (green) at cell-cell junctions is increased in shTln1 cells compared to shScramble HUVECs (scale=25 μm). E. Intensity profile plot of VE-Cadherin and vinculin immunofluorescence shown in D. (n=4) F. Inhibition of ROCK-mediated cellular contraction (Y-27623) reduces vinculin localization at cell-cell junctions of shTln1 HUVECs relative to vehicle treated cells (n=3; scale=25 μm). G. Intensity profile plot of VE-cadherin and vinculin immunofluorescence depicted in G (n=3). H. HUVEC monolayer resistance measured using electrical cell impedance sensing (ECIS) of shTln1 infected monolayers is reduced relative to shScramble (n=3; *p=0.0131; two-tailed unpaired t-test). I. HDMVEC monolayer resistance measured by ECIS of shTln1 infected monolayers is reduced relative to shScramble (n=3; *p=0.0399; two-tailed unpaired t-test).