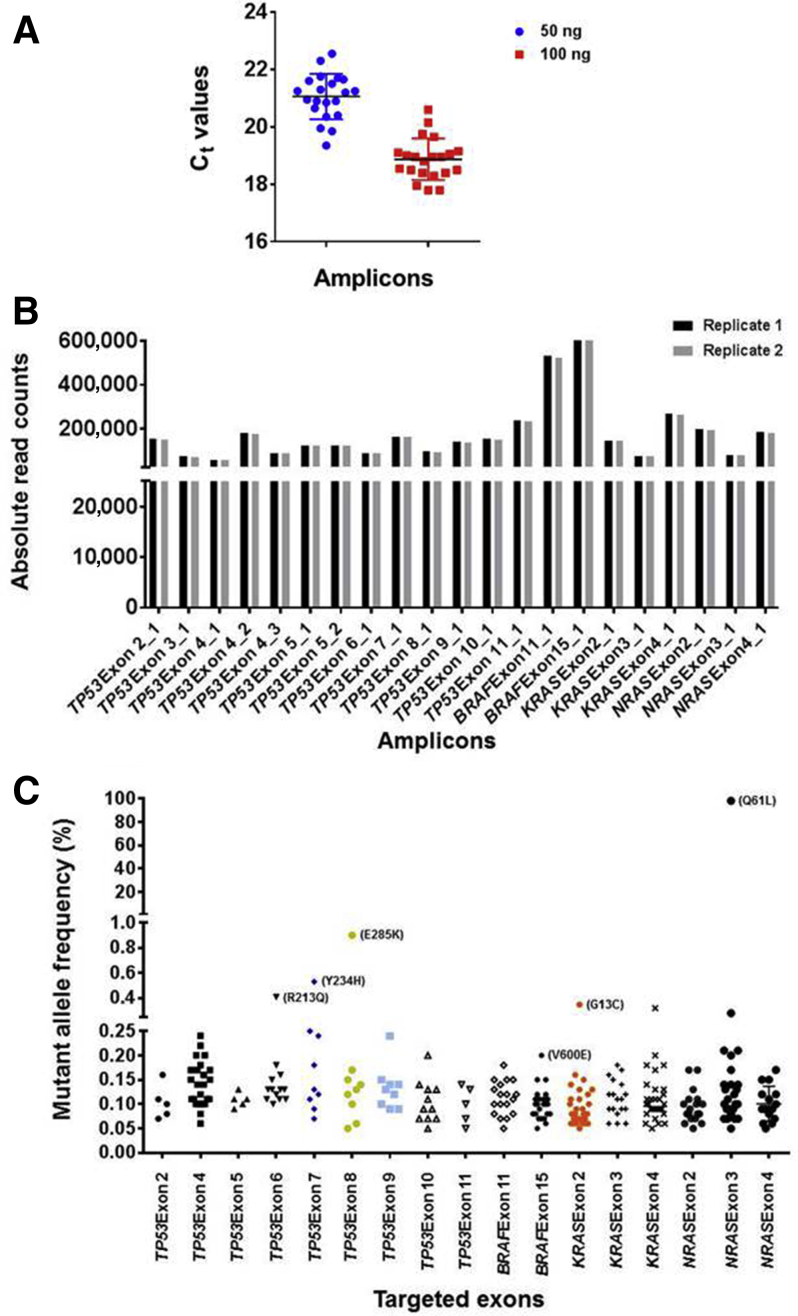
Figure 4.
Evaluation of molecular barcode–containing libraries by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS). A: qPCR evaluation of size-selected libraries indicate uniform representation of 21 amplicons in the libraries. Note that all amplicons were present within a 2- to 3-Ct value difference from the median. B: NGS indicates relatively uniform representation of the 21 amplicons in sequencing libraries. Libraries were sequenced in two independent runs, and the absolute read counts for each amplicon are depicted. C: An NGS data analysis without using molecular barcode information indicates the presence of abundant false-positive mutations at low frequencies. Libraries prepared from the reference DNA mix containing 98.4% (p.Q61L) NRAS, 1% (p.E285K) TP53, 0.5% (p.R213Q; p.Y234H) TP53, 0.5% (p.G13C) KRAS, and 0.1% (p.V600E) BRAF mutations were sequenced independently twice; the results of one sequencing run are shown. Note that the expected mutations above 0.3% allelic frequency were clearly apparent, although false-positive mutations appeared in this range within the amplicons covering KRAS exon 4 and NRAS exon 3. More false-positive mutations are observed between 0.05% and 0.3% allelic frequencies, and the true BRAF (V600E) mutation within this range is obscured by the false positives.