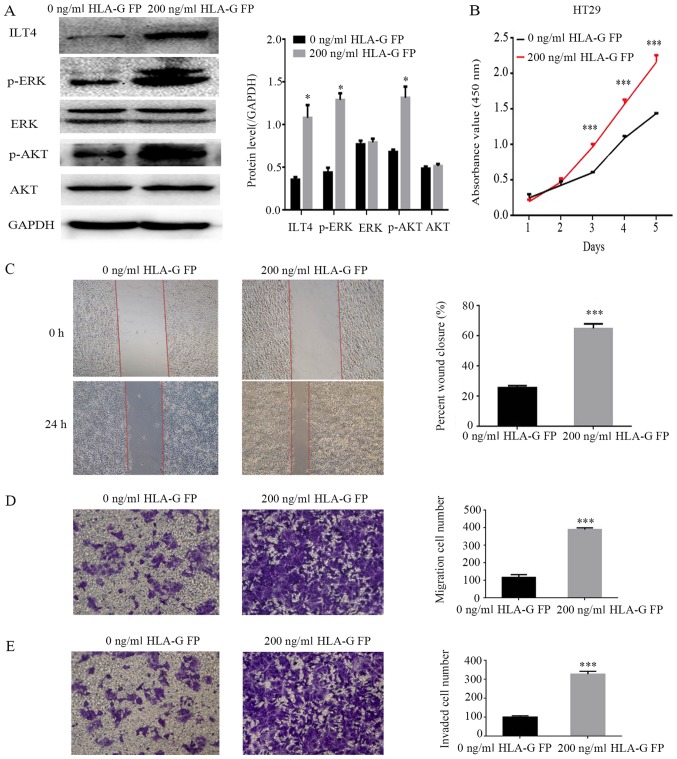
Figure 8.
Addition of HLA-G FP activates AKT and ERK signaling, and promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of HT29 cells. (A) Protein expres sion of ILT4, AKT, p AKT, ERK, p ERK and GAPDH in HT29 following the addition of HLA-G FP. PBS served as a negative control. (B) The effects of HLA-G FP on proliferation were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit 8 assays. The effects of HLA-G FP on migration were detected by (C) wound healing assay (magnification, ×40) and (D) Matrigel invasion assay (magnification, ×100). (E) The effects of HLA-G FP on invasion were measured by Matrigel invasion assays. Magnification, ×100. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 vs. cells with 0 ng/ml HLA-G FP. HLA-G, human leukocyte antigen G; ILT4, immunoglobulin like transcript 4; FP, fusion protein; p , phospho ; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; AKT, protein kinase B.