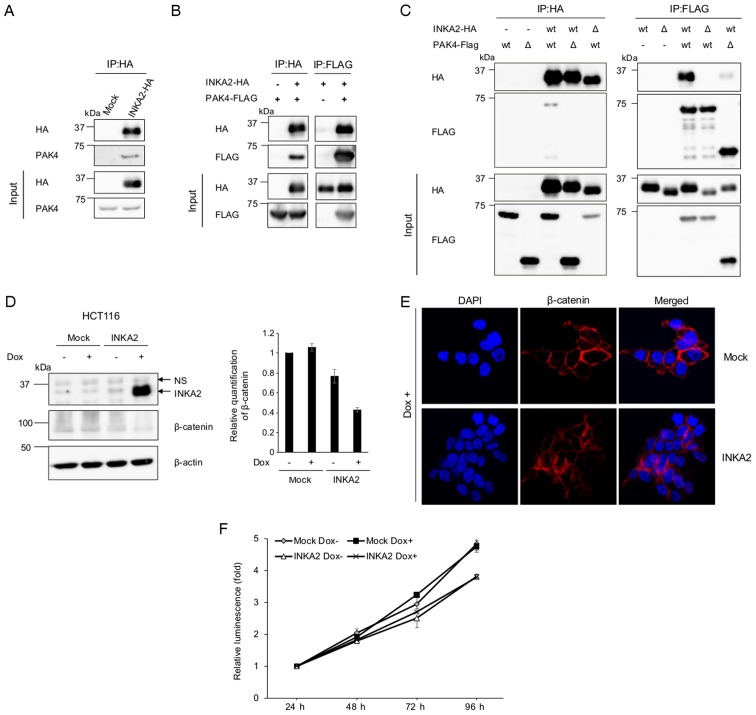
Figure 6.
INKA2 binds to the catalytic domain of PAK4 via the iBox domain and downregulates β-catenin. (A) The pCAGGSnHC empty vector (Mock) or pCAGGSnHC/INKA2 (INKA2-HA) plasmid were transfected into 293T cells. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and blotted with an anti-PAK4 antibody to identify the interaction. (B) The pCAGGSnHC/INKA2 (INKA2-HA) and pCAGGSn3Fc/PAK4 (PAK4-FLAG) plasmids were co-transfected into 293T cells. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody and blotted with anti-HA and anti-FLAG antibodies. (C) The deletion constructs shown in Fig. 5B were added during the co-transfection depicted in (B). Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody. Wt; wild-type. Δ; deleted versions: INKA2 Δ150-160 for INKA2, and PAK4 1-325 for PAK4. (D) Whole-cell lysates of the HCT116 cell line stably expressing INKA2 cultured in the presence of Dox were blotted with anti-INKA2 and anti-β-catenin antibodies. The bar chart represents the quantification of β-catenin proteins normalised to β-actin and untreated mock-expressing cells. β-Actin is shown as a loading control. Error bars are the means ± SD, n=2. (E) Immunocytohistochemistry of the stable HCT116 cell line cultured in the presence of Dox. Cells were stained with DAPI (blue) and an antibody against β-catenin (red). (F) ATP assay performed with the HCT116 cell line stably expressing INKA2 in the presence of Dox. The luminescence of each cell line were normalised to the measurement at 24-h time-point. Error bars are the means ± SD, n=2. INKA2, inka box actin regulator 2; Dox, doxycycline; PAK4, p21 (RAC1) activated kinase 4.