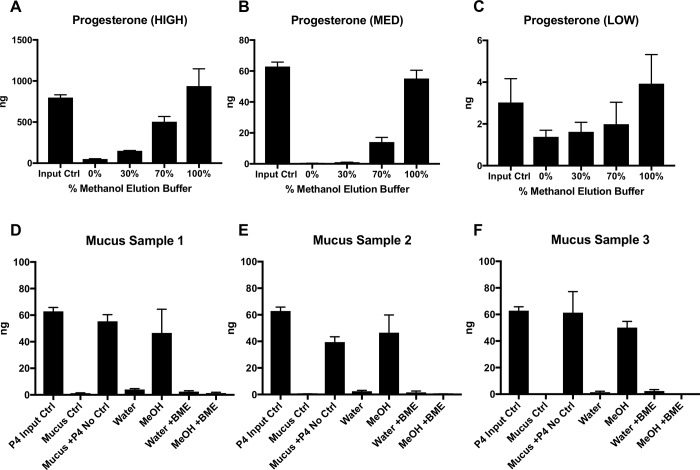
Fig 1. Optimization of progesterone elution from ophthalmic sponges.
(A-C) High (A; 500 ng), medium (B; 50 ng), and low (C; 5 ng) levels of progesterone were spiked onto ophthalmic sponges, and eluted with varying percentages of methanol in water. (D-F) 50 ng progesterone was spiked into 25 uL mucus from three subjects and then absorbed onto ophthalmic sponges. Sponges were eluted with water or methanol, with or without 0.5 mM beta mercaptoethanol (BME). Progesterone concentrations were measured by ELISA. Bars represent the mean progesterone levels ± standard deviations (SDs). Data are representative of 3 independent experiments each performed in duplicate. Student t tests were performed to compare input control levels to levels eluted from ophthalmic sponges. No statistically significant differences were noted between any groups.