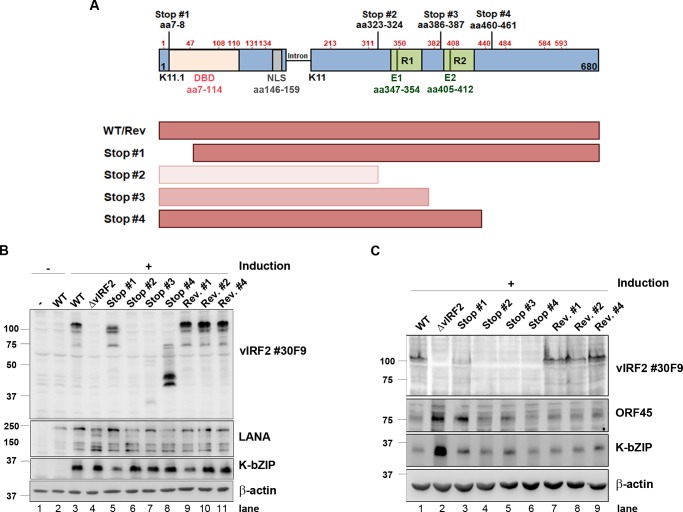
Fig 6. Domains of vIRF2 required for the inhibition of early lytic KSHV protein expression.
(A) Schematic diagram of the possible vIRF2 protein forms expressed from KSHV ORFs K11.1 and K11 in different vIRF2 double stop mutants compared to the WT-infected cells. Methionine residues are indicated by red amino acid numbers at the positions aa1, 47, 103, 110, 131, 134 in K11.1 and aa213, 311, 350, 382, 408, 440, 484, 584, 593 in K11. Lines indicate double stop mutations at the positions aa7-8, aa323-324, aa386-387 and aa460-461, DBD: DNA binding domain (aa7-114), NLS: nuclear localization signal (aa146-159), R1/R2: repeat region 1/2, E1/E2: antibody epitope. (B) The different stable HEK-293.BAC16 cell lines were induced using 10% tissue culture supernatant containing RTA-expressing baculovirus and 1.67 mM SB. Protein expression was analyzed 72 h post induction by WB after lysis. (C) The different stable HuARLT.BAC16 cells were induced using 12.5% tissue culture supernatant containing RTA-expressing baculovirus and 1.67 mM SB for 72 h. Protein expression was analyzed by WB after lysis of the cells. Stop #1, aa7-8; Stop #2, aa323-324; Stop #3, aa386-387; Stop #4, aa460-461. Rev. #1, revertant to Stop #1; Rev. #2, revertant to Stop #2; Rev. #4, revertant to Stop #4.