FIGURE 4.
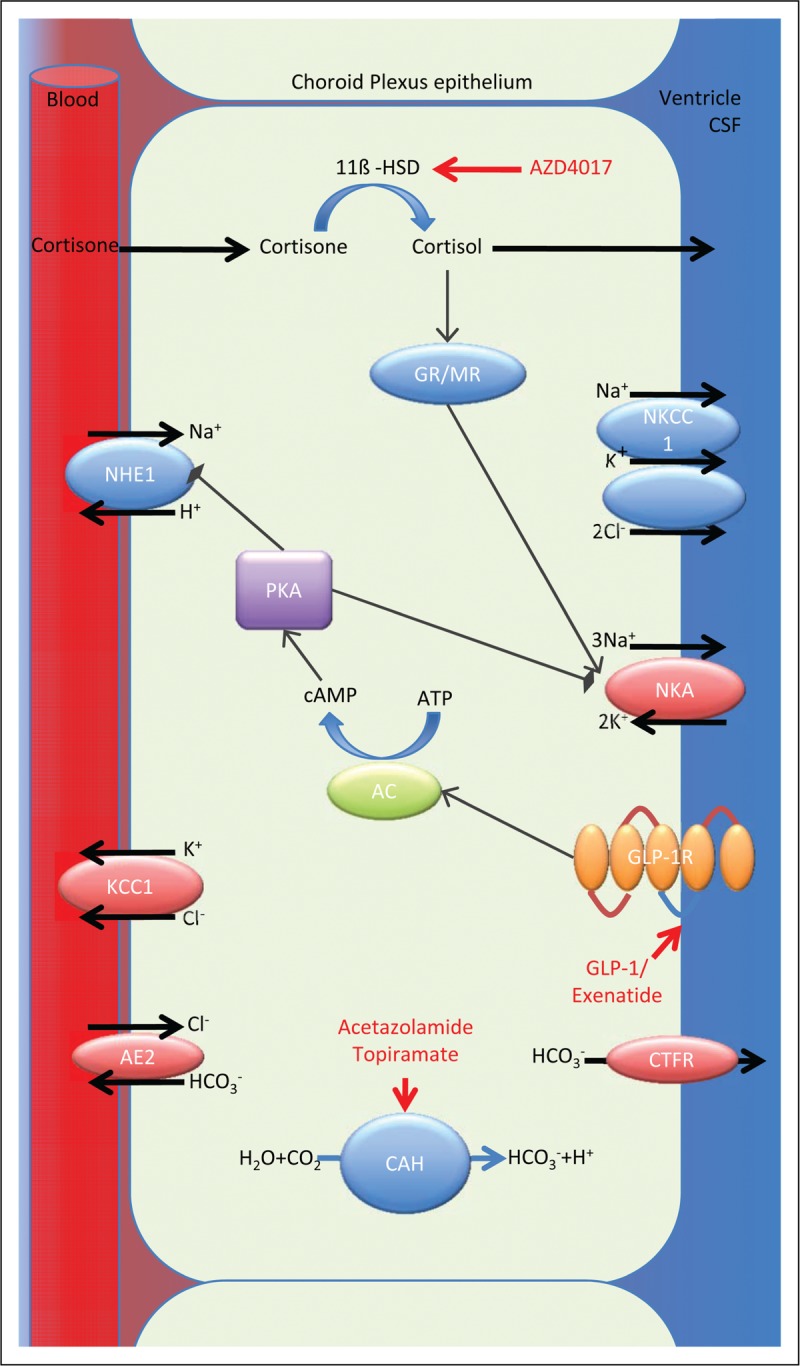
The major ion channels responsible for CSF secretion in the choroid plexus are shown with sites of action of acetazolamide, AZD4017 and exenatide. Cortisone is converted to the active cortisol by 11ß-HSD1, cortisol binds to the GR and MR receptors, which upregulate Na+ K+ ATPase activity; AZD4017 inhibits 11ß-HSD1 reducing local availability of cortisol. Exenatide binds and activates GLP-1R stimulating the conversion of ATP to cAMP by AC. cAMP activates PKA, which inhibits the Na+ H+ exchanger reducing Na+ re-absorption and also inhibits the Na+ K+ ATPase reducing Na+ excretion. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the conversion of H2O and CO2 to H+ and HCO3−, which is important in the establishment of the osmotic gradient. Both acetazolamide and topiramate inhibit carbonic anhydrase function. AC, adenylate cyclase; AE2, anion exchange protein 2; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; CTFR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide 1; GLP-1R: glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor; 11ß-HSD, 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1; GR/MR, glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors; KCC1, K-Cl cotransporter 1; NHE1, Na-H antiporter; NKA, N-K ATPase; NKCC1, Na-K-Cl cotransporter; PKA, protein kinase A.
