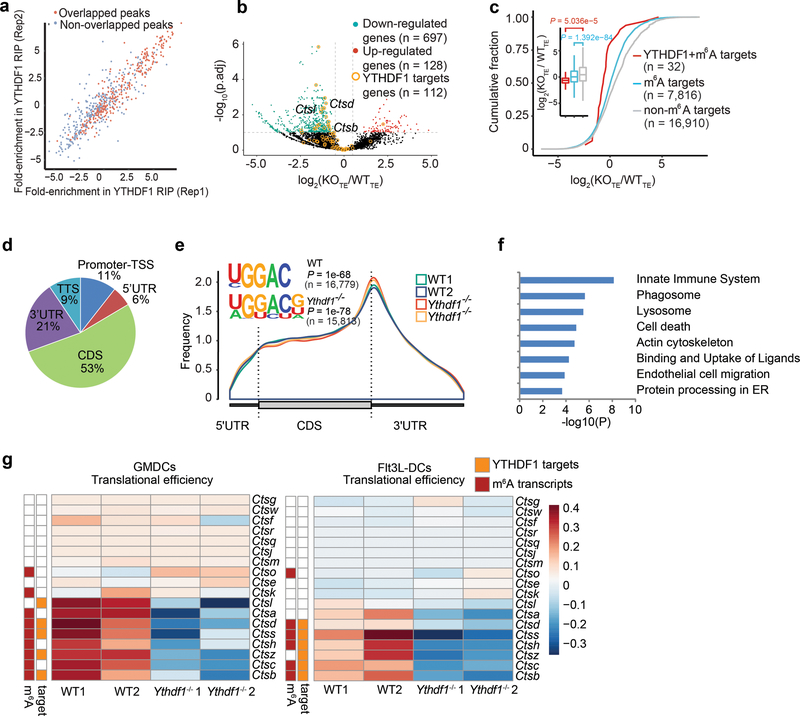
Extended Data Fig. 7 |. YTHDF1-deficient GMDCs exhibit lower translational rates.
a, High reproducibility of YTHDF1 RIP-seq data in GMDCs. For each potential YTHDF1 binding peak, the fold-enrichment of RIP/Input signal was determined for both Replicate 1 and Replicate 2. The peaks identified in both replicates were considered as high-confidence peak and indicated in red. b, Volcano plots of genes with differential translational efficiency in WT and Ythdf1−/− GMDCs. YTHDF1 targets were marked with yellow circles. P values were calculated by two-sided likelihood ratio test and adjusted by Benjamini & Hochberg method; n = 4 (2 conditions x 2 biological replicates) c, Cumulative distribution log2FoldChange of translational efficiency between WT and Ythdf1−/− GMDCs. P values were calculated by two-sided Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; n = 2 independent biological replicates. Box-plot elements: centre line, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; whiskers, 1–99%. d, Pie charts presenting the distribution of YTHDF1-binding sites in transcripts. e, Metagene-plot depicting nearly unchanged m6A peaks distribution and similar consensus motifs in WT and Ythdf1−/− GMDCs. P values of consensus motifs were generated by HOMER31 with one-sided binomial test. f, KEGG and GO enrichment analysis of YTHDF1 target genes revealed enrichment of biological functions related to innate immune system, lysosome and phagosome (n = 79). One-tail hypergeometric test was used to determine statistical significance of enrichment. g, Heatmap showing translational efficiency of cathepsin genes in GMDCs and Flt3L-DCs. n, numbers of genes or m6A peaks.