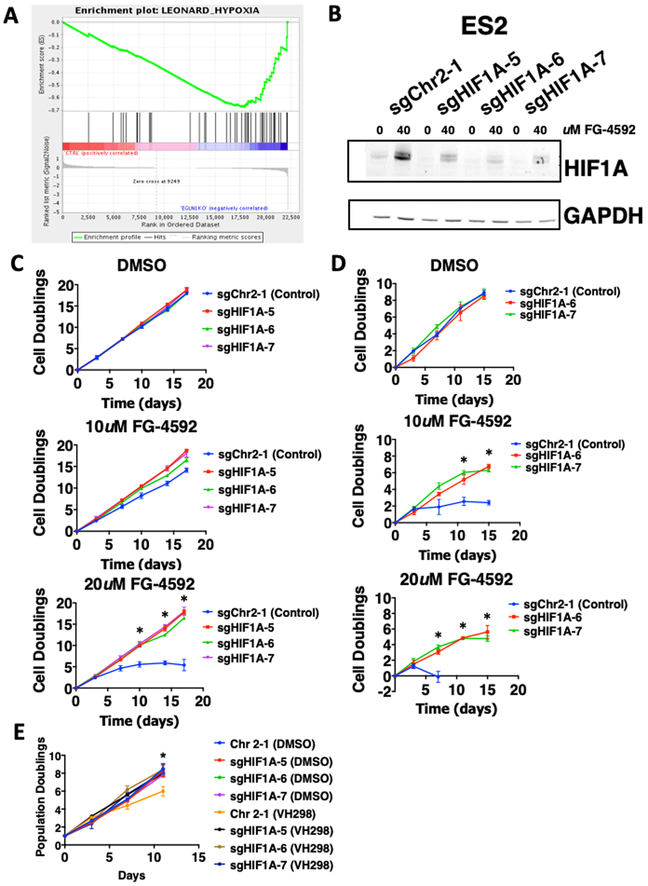
Figure 5. Depletion of HIF1A rescues cells from EGLN1-dependency.
A. RNA sequencing performed on ES2 and OVISE wild-type cells compared to ES2 and OVISE EGLN1 knockout cells. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of RNA sequencing data shows that HIF1A-related pathways are affected in EGLN1 KO cells.
B. Immunoblot showing efficiency of control sgRNAs (sgChr2–1) or HIF1A deletion with sgRNAs (sgHIF1A-5, sgHIF1A-6, sgHIF1A-7) 48 hours post treatment with control (DMSO) or EGLN1 inhibitor (FG-4592).
C. EGLN1-dependent ES2 cells are resistant to EGLN1 inhibition after HIF1A knockout. DMSO treatment (top) has no effect on control or HIF1A-knockout cells. Increasing treatment with FG-4592 (10 uM middle, 20 uM bottom) reduces proliferation of control cells (blue) but not HIF1A-knock. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments and data is graphed as mean ± standard deviation of 3 replicates. *p<0.05
D. EGLN1-dependent OVISE cells are resistant to EGLN1 inhibition after HIF1A knockout. Similar to ES2 cells, DMSO treatment (top) has no effect on control or HIF1A-knockout cells. Increasing treatment with FG-4592 (10uM middle, 20uM bottom) reduces proliferation of control cells (blue). Results are representative of 2 independent experiments and data is graphed as mean ± standard deviation of biological triplicates. *p<0.05
E. EGLN1-dependent ES2 cells are resistant to VHL1 inhibition after HIF1A knockout. Treatment with 100uM of VH298 significantly reduces proliferation of control cells (orange) compared to HIF1A knockout cells. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments and data is graphed as mean ± standard deviation of biological triplicates. *p<0.05