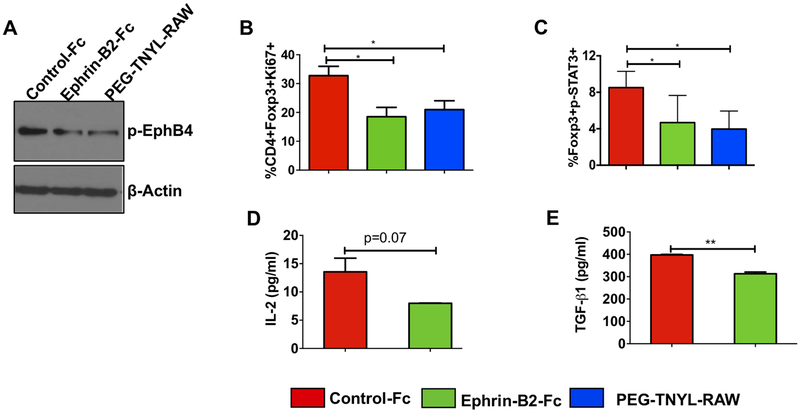
Figure 3. Treatment with a high (inhibitory) concentration of ephrin-B2-Fc reduces Ki67-expressing Tregs, STAT3 phosphorylation, and TGF-β1 and IL-2 levels in Tregs in vitro.
Western blot analysis of isolated CD4+ T cells treated with 20 μg/ml ephrin-B2-Fc for 72 hours shows a decrease in EphB4 tyrosine phosphorylation as compared to the control treatment group (2.5 μg/ml). PEGylated TNYL-RAW (EphB4 antagonist) show similar effect (A). Flow cytometry analysis of T cells demonstrates decreased Ki67-expressing Tregs (CD4+Foxp3+Ki67+) following a 48 hour treatment with a high dose (20 μg/ml) of ephrin-B2-Fc or PEG-TNYL-RAW (4.5 μg/ml) (B). The concentration of 20 μg/ml ephrin-B2-Fc has an inhibitory effect on p-STAT3 at the 24 hours time-point, similar to 4.5 μg/ml PEG-TNYL-RAW (C). Conditioned media collected at 24 hours from Tregs treated with control-Fc, and 20 μg/ml ephrin-B2-Fc were subjected to TGF-β1 ELISA assay or to a U-plex mesoscale cytokine array to determine change in secreted IL-2 levels (D) and TGF-β1 levels (E). Data represent mean ± SEM. The Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA were used to calculate the significance of differences between the groups.*p<0.05, **p=0.001–0.01.