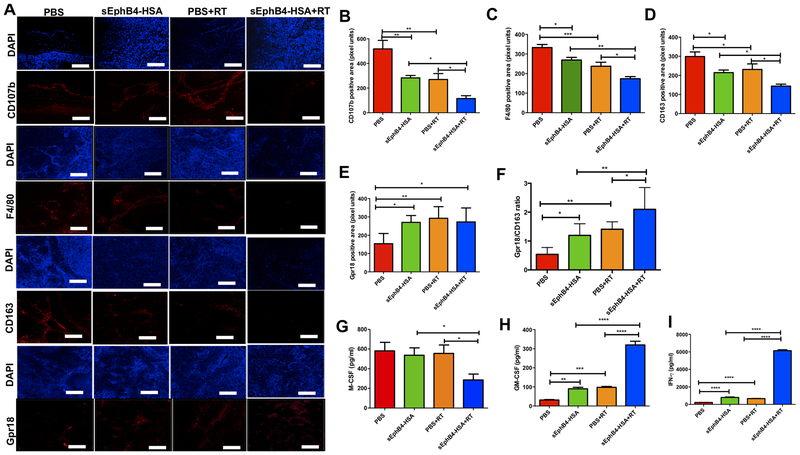
Figure 6. Targeting of EphB4-ephrin-B2 interaction combined with radiation decreases tumor-associated M2 macrophages in PDX models of HNSCC.
Immunofluorescence analysis shows decreased CD107b, F4/80, CD163, and increased Gpr18 staining in CUHN013 tumors treated with sEphB4-HSA and RT compared to single agents or the PBS control group (A). CD107b and F4/80 represent pan-macrophage markers, CD163 is a specific marker for M2 macrophages and Gpr18 is a marker for M1 macrophages. Quantitative analysis for different macrophage markers is shown in (B-F). Significant changes in the levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are evident in plasma samples in vivo when EphB4-ephrin-B2 inhibition is combined with RT. Plasma samples were collected 96 hours after RT from the mice implanted with CUHN013 tumors and treated with PBS, sEphB4-HSA, PBS and RT, or sEphB4-HSA and RT and analyzed using a mouse cytokine array (G-I). One-way ANOVA was used to calculate the significance of the differences between the groups. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p=0.001–0.01, ***p=0.0001–0.001, ****p<0.0001. Scale bar: 100 μm.