Figure 6. Knockdown of MALAT1 enhances the anti-glioma effect of TMZ.
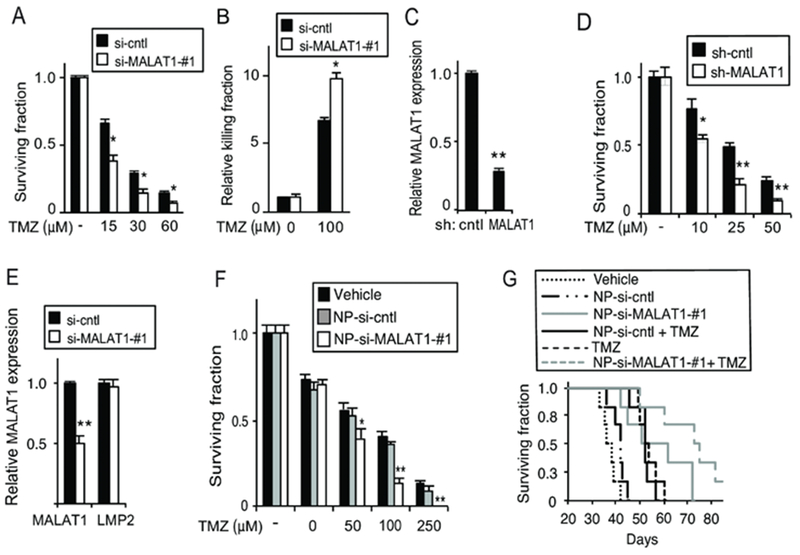
(A) Clonogenic assay in U87 cells transfected with si-cntrl or si-MALAT1-#1 treated as shown. (B) Trypan blue assay in GBM34 GSCs transfected with si-cntrl or si-MALAT1-#1 following treatment with TMZ for 72 hours. (C) MALAT1 expression in U87 cells following infection with the indicated sh-RNA construct. (D) Clonogenic assay in U87 cells expressing sh-control or sh-MALAT1 treated with TMZ. (E) qPCR analysis of MALAT1 and LMP2 mRNA expression, relative to GAPDH, in U87 cells treated with nanoparticles carrying si-control (NP-si-cntrl) or si-MALAT1 (NP-si-Malat1). (F) Clonogenic assay in U87 cells following treatment with the indicated nanoparticles. (G) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of mice bearing intracranial U87 GBM xenografts (n= 6 mice per group) following treatment with TMZ (days 4, 7 and 10) and/or the indicated NP. P < 0.02, Log-rank: TMZ + NP-si-MALAT1-#1 vs. TMZ + NP-si-cntl or NP-si-MALAT1-#1 alone. Trypan blue, clonogenic, qPCR data represent mean ±SD of triplicate samples, repeated with similar findings. *, p< 0.05; **, p< 0.01 relative to control.
