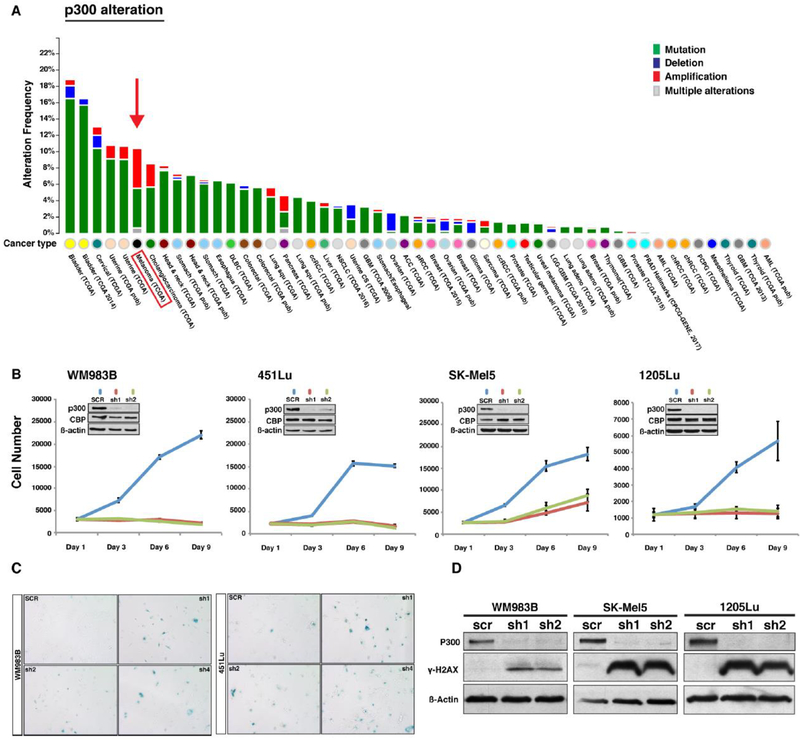
Figure 1. Genetic alteration frequency of EP300 gene in human cancers and functional assessment of the p300 in melanoma cell lines.
(A) EP300 gene alteration frequency in various human cancers available in the TCGA data set. Melanoma is the cancer type displaying the highest EP300 gene alteration frequency. (B) Functional role of p300 in melanoma cell growth. EP300 expression was silenced by shRNAs in four melanoma cell lines (WM983B, 451Lu, SK-Mel5, and 1205Lu) and subjected to a cell proliferation assay. Insert demonstrates p300 knockdown efficiency via western blot. (C) Senescence-associated ß-galactosidase staining assay of p300 silenced melanoma cell lines. ß-galactosidase staining positive cell numbers were increased after p300 depletion in 451Lu and WM983B cells when compared to those of control. (D) Western blot analysis of cellular senescence marker γ-H2AX. p300-depleted melanoma cells were assayed for activation of the cellular senescence response using antibody against phosphorylated H2AX. (E) Cell cycle profile analysis of p300-depleted melanoma cells (1205Lu and 451Lu). Error bars, SD; *p<0.05.