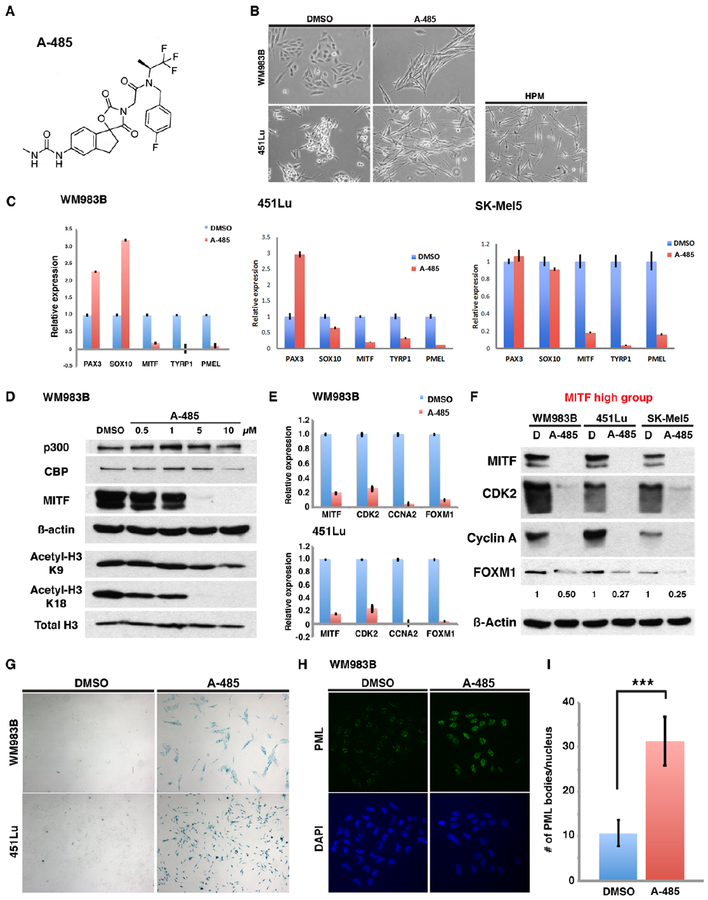
Figure 6. Chemical inhibition of p300 HAT activity by a potent and selective inhibitor promotes melanoma senescence through suppression of the p300/MITF/FOXM1 transcriptional axis.
(A) Chemical structure of A-485*. (B) Cell morphology changes following A-485* treatment of melanoma cells (5 μM) for 72 hours. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of MITF and melanocyte differentiation-associated genes following treatment of melanoma cells with A-485*. (D) Western blot of p300-dependent histone acetylation and MITF expression in melanoma cells following treatment A-485*. (E and F) Relative mRNA and protein levels of MITF, CDK2, CCNA2 and FOXM1 in melanoma cells following treatment with A-485* (10 μM) for 5 days. (G) Senescence-associated ß-galactosidase staining of melanoma cells treated with A-485* (10 μM) for 7 days. (H) Immunofluorescence staining of the cellular senescence protein, PML, in melanoma cells treated with A-485* (10 μM) for 7 days. (I) Quantification of PML bodies in melanoma cells following A-485* treatment. Error bars =1 SD; ***p<0.001.