Figure 2.
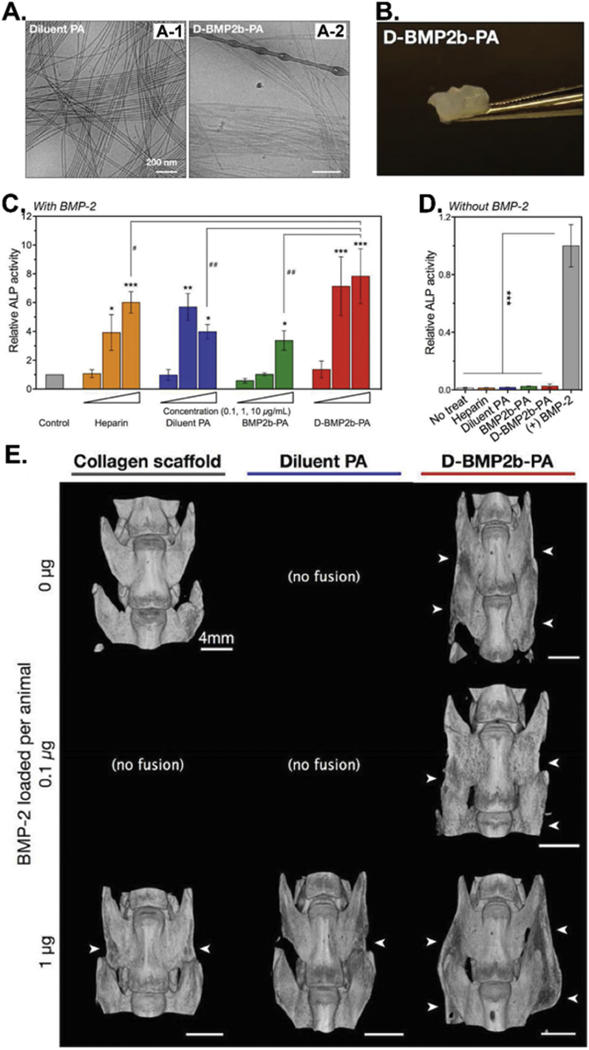
BMP-2-binding peptide functionalized amphiphile (PA) nanofibers (D-BMP2b-PA) as biomaterials for BMP-2 absorption and in vivo spinal fusion (bone forming). (A) Cryo-TEM images of the filamentous morphologies of the diluent PA (A-1) and the diluted BMP-2-binding PA (D-BMP2b-PA) (A-2). (B) Photograph of the self-supporting D-BMP2b-PA gel. (C&D) ALP enzyme activities of the BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation of C2C12 pre-myoblasts after 4 days of culturing in the presence (C) or absence (D) of BMP-2 or without BMP-2. Measurements were normalized to their respective DNA content, and the final average values from treatments are normalized to control treatment with BMP-2 alone. The results showed that D-BMP2b-PA gel could capture and retain BMP-2 molecules and significantly enhanced the BMP-2-induced osteogenesis of C2C12 cells in the presence or absence of BMP-2. (E) Micro-CT images of representative spine fusions showing that D-BMP2b-PA efficiently induced the fusion of spine. White arrows indicate the presence of fusion mass in the transverse processes. (Reprinted with permission from ref. [53], copyright 2015, Wiley)
