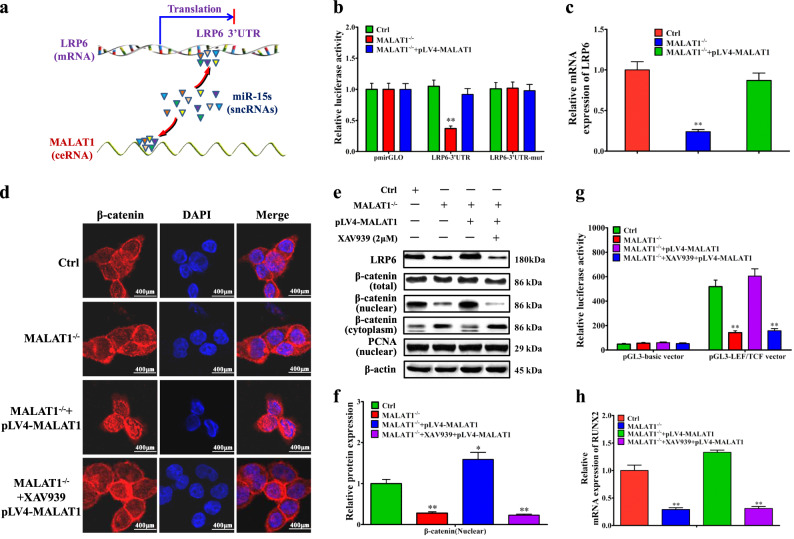
Fig. 4. MALAT1 promotes the RUNX2 transcription through LRP6-mediated β-catenin signaling pathway.
a Schematic diagram of the interlink between MALAT1 and miR-15s or between miR-15s and LRP6. b Luciferase reporter activities of wild-type mutant LRP6 3′UTR reporter, and empty constructs in LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells and pLV4-MALAT1-transfected LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells. c Real-time PCR assay of LRP6 mRNA levels in LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells and pLV4-MALAT1-transfected LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells. d Immunofluorescence detection of β-catenin LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells and pLV4-MALAT1-transfected LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells. e–f Western blot and quantitative assay of β-catenin (nuclear) in LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells and pLV4-MALAT1-transfected LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells. g LEF/TCF promoter activity assay in LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells and pLV4-MALAT1-transfected LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells. h Real-time PCR assay of RUNX2 mRNA levels in LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells and pLV4-MALAT1-transfected LoVo/MALAT1−/− cells. XAV939, the inhibitor for β-catenin signaling pathway, was used to block the activation of β-catenin signaling pathway and observe whether there was any effect of MALAT1 through the β-catenin signaling pathway. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (t test)