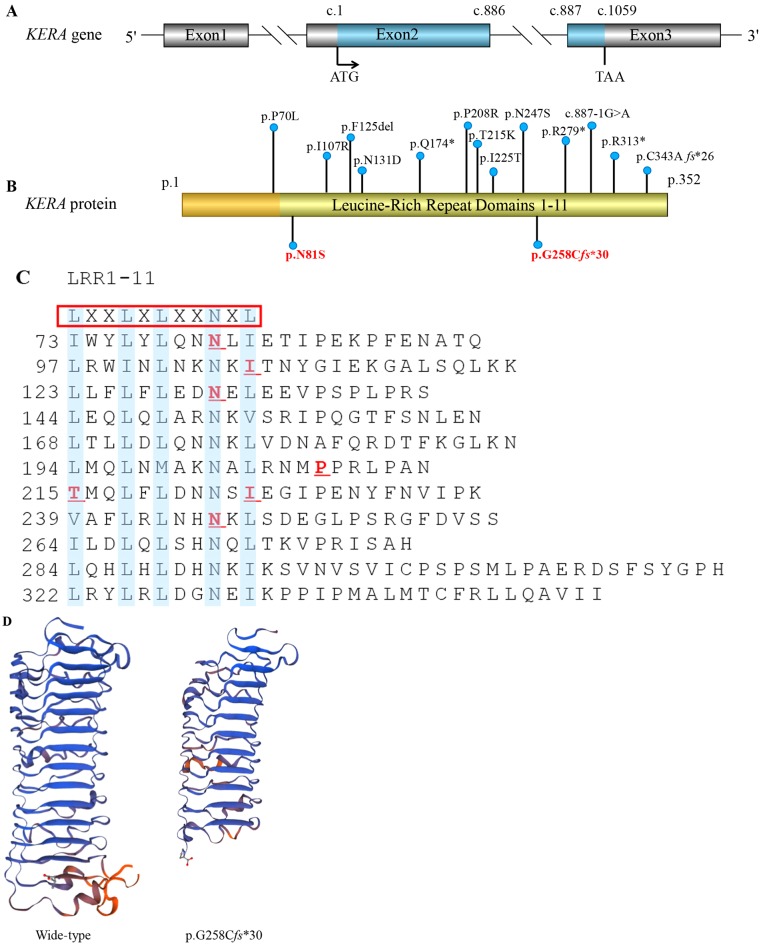
Figure 2.
KERA mutations associated with cornea plana. (A) The structure of the KERA gene. It contains three exons and two introns; the blue marker indicates the translation area, which forms a precursor protein of 352 amino acids. ATG: Initiation codon; TAA: Stop codon. (B) Kera protein schematic, including locations of the variations that have previously been reported. In the present study, amino acid position 81 was changed from asparagine (Asn, N) to serine (Ser, S). The p.G258Cfs*30 mutation leading to premature termination codon is indicated in bold red. Apart from p.P70L, all mutations associated with the disease are located in the LRR domains. (C) The blue highlighting indicates the consensus motifs LXXLXLXXNXL, which form 11 LRR domains. The red underlining indicates the six missense mutations previously identified. (D) Mutant Kera (p.G258Cfs*30) was predicted by Swiss-Model online software to result in the loss of the partial LRR domain and the C-terminal domain, compared with the wild type protein. LRR, leucin-rich repeat; Kera, keratocan.