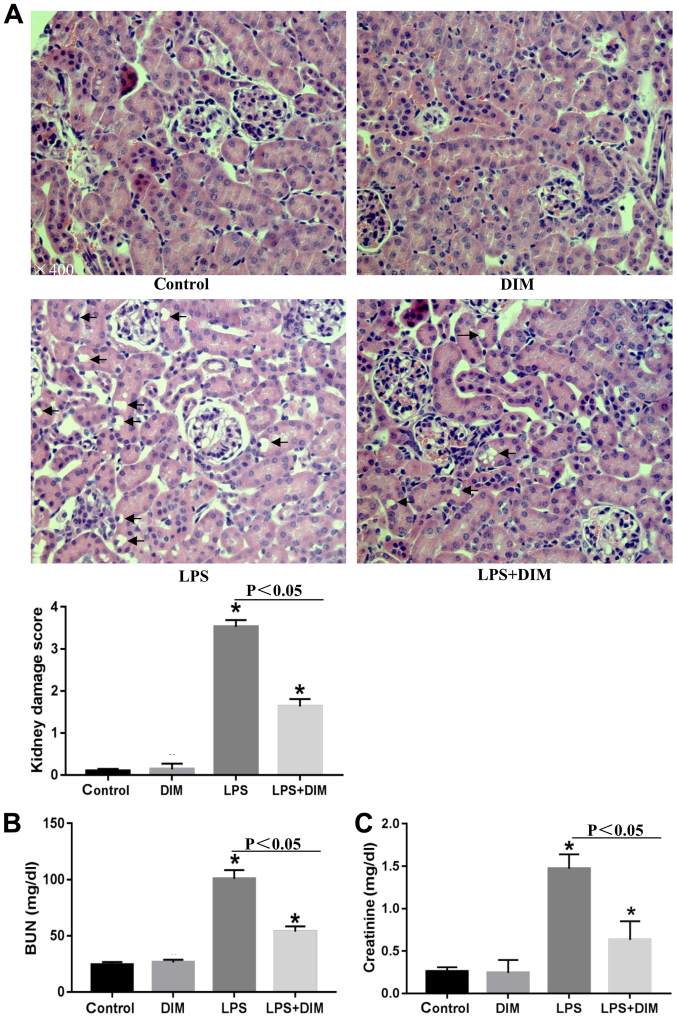
Figure 1.
DIM mitigates histopathological changes and restores renal function in an LPS-induced acute kidney injury mouse model. (A) Mice were exposed to LPS (10 mg/kg), DIM (40 mg/kg), or LPS + DIM (10 mg + 40 mg) for 24 h; histological changes in kidneys were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. (B) BUN levels were determined after the mice were exposed to LPS, DIM or LPS + DIM for 24 h. (C) Blood creatinine levels were determined after the mice were exposed to LPS, DIM or LPS + DIM for 24 h. The arrows indicate damaged tubular epithelial cells. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 vs. control. DIM, 3,3′-diindolylmethane; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; BUN, blood urea nitrogen.