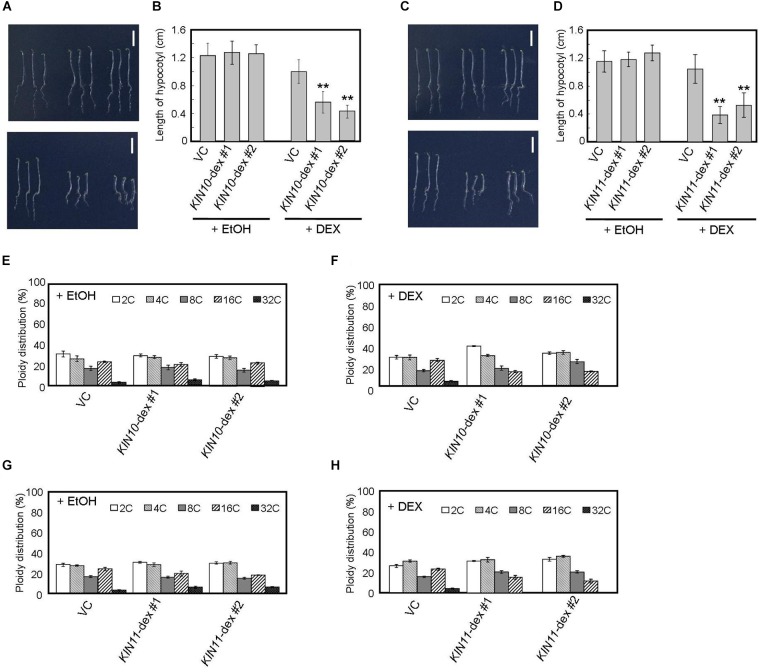
FIGURE 2.
DEX-inducible KIN10 and KIN11 over-expression plants have decreased polyploidy levels in dark. (A,B) Phenotype of 5-day-old seedlings of vector control (VC), KIN10-dex #1, and KIN10-dex #2 grown on medium containing EtOH (A, upper panel) and 2 mg/ml DEX (A, bottom panel) in the dark. (B) The average of hypocotyl length of vector control (VC), KIN10-dex #1, and KIN10-dex #2. 80–100 seedlings were measured. (C,D) Phenotypes of 5-day-old seedlings of vector control (VC), KIN11-dex #1, and KIN11-dex #2 grown on medium containing EtOH (C, upper panel) and 2 mg/ml DEX (C, bottom panel) in the dark. (D) The average of hypocotyl length of the vector control (VC), KIN11-dex #1, and KIN11-dex #2. 80–100 seedlings were measured. (B,D) Error bars indicate standard deviation. Asterisks indicate significance at P < 0.05 by t-test when compared to VC. (E,F) Relative ratio of each ploidy of dark-grown hypocotyls of VC, KIN10-dex #1, and KIN10-dex #2 grown on medium containing EtOH (E) and 2 mg/ml DEX (F) in the dark. Approximately 20 seedlings were used in ploidy analysis. (G,H) Relative ratio of each ploidy of dark-grown hypocotyls of VC, KIN11-dex #1, and KIN11-dex #2 grown on medium containing EtOH (G) and 2 mg/ml DEX (H) in the dark. Approximately 20 seedlings were used in ploidy analysis. (E–H) Error bars indicate standard error of five biological replicates.